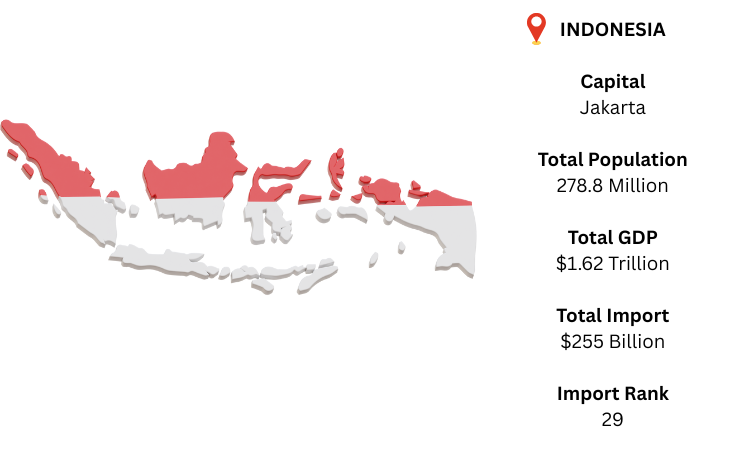
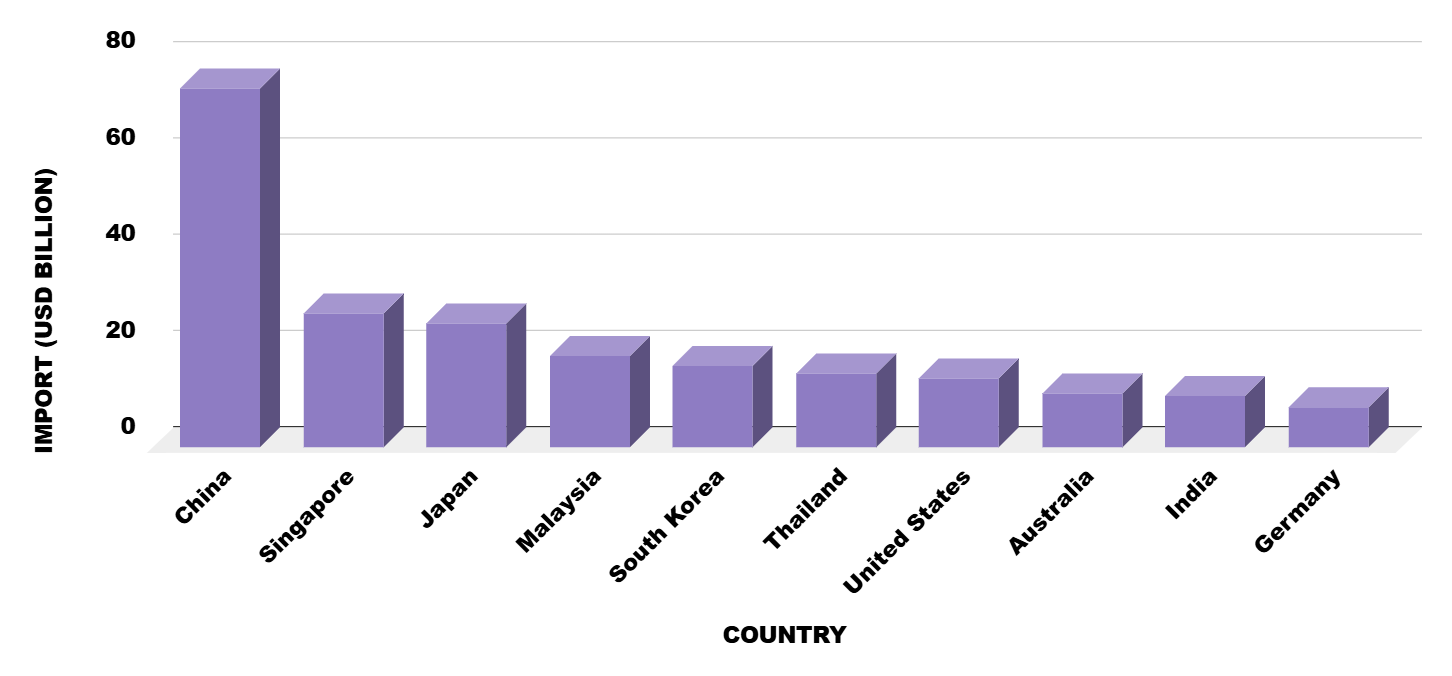
With more than 17,000 islands, Indonesia is the biggest archipelagic nation in Southeast Asia. Jakarta is the country's vibrant capital and commercial center. It is well situated between the Indian and Pacific Oceans and borders Malaysia, Papua New Guinea, and Timor-Leste on land. As one of the most active developing economies, Indonesia is expected to have a GDP of USD 1.62 trillion in 2024. Indonesia is the world's 29th-largest importer, according to Indonesia Global Import data. China is Indonesia's largest exporter, according to the Indonesia import data, offering a variety of products such as electronics, machinery, and raw materials. In 2024, Indonesia is expected to import a total of USD 255 billion anticipated by Import Globals a leading Indonesia Import Data provider.
Refined petroleum is the most popular import among the different goods, indicating Indonesia's ongoing need for industrial and energy inputs. As per the Indonesia customs data, Indonesia still depends heavily on imports to meet its energy, technological, and infrastructure needs, even though it produces a lot of goods domestically in a few industries. Being a member of ASEAN and a G20 economy, Indonesia is closely linked to both regional and international trade networks. Its trading ecology has been further strengthened by recent policy reforms in import facilitation, port infrastructure, and customs.