
- May 28, 2025
A New Era of Green Dominance: China's Clean Tech Exports to Emerging Markets Surged
Developing nations from Asia to Latin America are increasingly looking to China for high-quality, reasonably priced green technologies. According to an Import Globals Research on China Export Data, this rapid expansion is changing the dynamics of international commerce and posing both new possibilities and difficulties for global companies. Let's examine in detail how China is guiding clean technology in emerging markets.
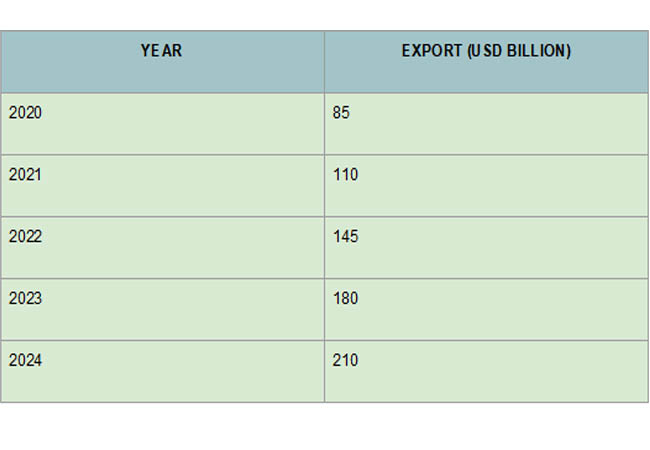
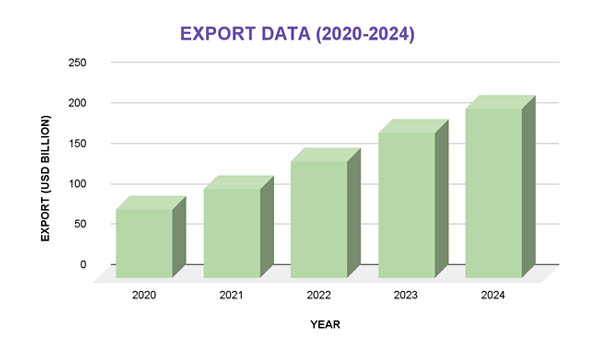
Growth in Clean Tech Exports (2020–2024)
According to Import Globals on China Export Data, China's exporting of clean technology is nothing short of extraordinary.
2020: The total value of clean technology exports was estimated at $85 billion.
2021: The post-pandemic rebound drove the figure up to $110 billion.
2022: A significant increase to $145 billion, with a 64% annual growth in solar PV exports.
2023: Exports of clean technology topped $180 billion.
2024: China's clean technology exports hit a record-breaking $210 billion, of which $90 billion went to emerging economies.
According to Import Globals' China Export Data, China's solar exports increased by an astounding 64% in 2022, reaching $52 billion. Even more remarkable is the fact that, for the fourth year in a row, China's exports of solar PV products topped 200 billion yuan, or about $27.38 billion. China was the source of more than 70% of the world's solar panels by 2024.
Furthermore, in 2024, China delivered more than 6.8 million EVs worldwide, with around 2.8 million of those shipments going to developing nations.
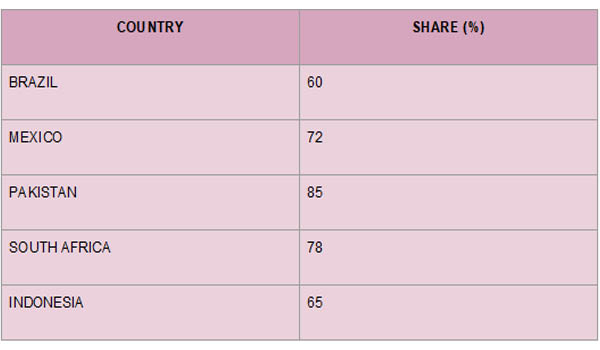
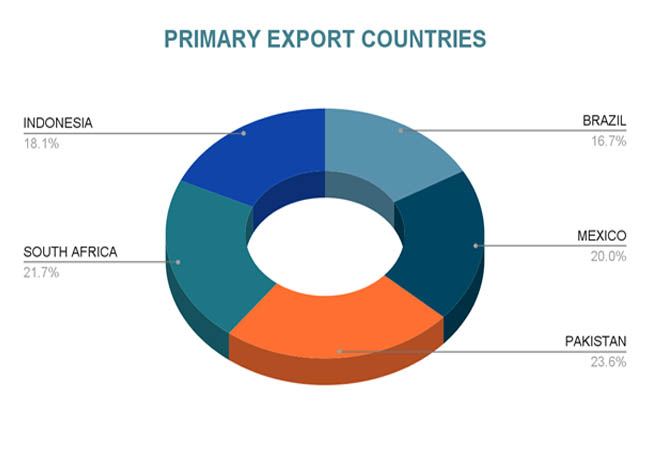
Primary Export Countries
China's green revolution has mostly benefited emerging countries in Asia and Latin America. About 70% of electric cars and 99% of solar panels in Latin America are made in China, which also dominates the import market for clean technology. A research by Import Globals on China Export Import Global Trade Data states that, mostly as a result of Chinese imports, these areas' renewable energy capacity increased by an average of 25–30% annually. Among the important locations were:
Brazil: 60% of Brazil's new solar capacity was imported from China.
Mexico: In 2024, 72% of EV imports came from China.
Pakistan: Chinese technology was used in 85% of new renewable projects.
South Africa: 78% of installations were Chinese solar panels.
Indonesia: 65 percent of new EV fleets were provided by Chinese businesses.
Export Categories for Clean Technology
China's clean tech exports in 2024 encompassed a wide range, according to a report by Import Globals on China Import Export Trade Data. Every area highlights China's approach of supplying innovative, affordable technology in addition to producing in large quantities.
Solar photovoltaics: Products related to solar photovoltaics (PV) have been steadily growing, surpassing $27 billion for four years. 78.1% of the world's solar panel shipments came from China.
Wind Turbines: 55% of new wind installations worldwide are exported, a 70% increase.
Lithium Batteries: Attained a $40 billion worldwide export share, or 24.1%.
Electric vehicles (EVs): In emerging markets alone, more than 2.8 million electric vehicles (EVs) are exported.
Bicycles and Electric Motorcycles: For the first time, export values surpassed 40 billion yuan ($5.5 billion).
Energy Storage Systems: Exported for $8 billion, mostly to Africa and Southeast Asia.
Pricing Trends
Pricing is one of China's most powerful tools in its clean tech invasion. As per China Export Import Global Trade Data provided by Import Globals, in 2024, a typical Chinese solar panel would cost around $0.18 per watt, while American manufacturers would charge $0.29 per watt. Chinese EV battery packs cost about $100/kWh, whereas European ones cost $150/kWh. China's manufacturing expenses are far cheaper than those of its international counterparts. Manufacturing battery technology, wind turbines, and solar PV modules is:
40% more costly in the United States.
In the EU, prices are 45% higher.
In India, prices are 25% higher.
Because of their cost advantage, Chinese companies are able to provide extremely inexpensive rates without sacrificing quality, which makes their goods especially appealing to emerging nations that are keen to adopt green energy at affordable prices.
But according to Import Globals' Research on China Exporter Data, this has raised a lot of worry in developed countries. While the EU is thinking about taking similar steps, nations like the U.S. and Canada have imposed 100% tariffs on electric vehicles built in China. The fundamental concern is that indigenous clean tech industries in other regions of the world may be suppressed by Chinese dominance.
Projected Patterns and Strategic Consequences
China's clean technology trajectory points to a range of potential advantages and disadvantages going forward:
Overcapacity Risk: According to Import Globals on China Import Export Global Data, China's solar PV production capacity is predicted to reach 1.2 terawatts by 2025, which is significantly more than the 500 gigawatts of forecasted worldwide demand.
Global Investment Expansion: In an effort to get around any trade restrictions and set up regional manufacturing centers, Chinese clean tech businesses have declared intentions to spend an estimated $100 billion abroad since 2023.
Green Finance Push: By providing low-interest loans to partner nations to encourage the use of clean technology, China is extending its green finance capabilities.
Market instability: Local businesses in importing nations may be weakened by the flood of cheap Chinese goods, which might result in political and economic backlash.
New Belt and Road Green Strategy: China's Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) 2.0 saw the signing of almost 40 new agreements devoted exclusively to green energy cooperation, according to China Export Data From Import Globals.
Global Leading Exporters of Clean Tech
Despite its dominance, China is not the only country in the world market for clean technology exports:
Conclusion
An important turning point for the global energy industry will be the spike in China's clean technology exports to emerging economies in 2024. According to China Export Import Global Trade Data, China is influencing the sustainable futures of innumerable countries in addition to growing its trade footprint by providing high-quality, reasonably priced green technology.
Emerging economies gain from economic development, but there are also strategic concerns, such as the instability of the world market and escalating geopolitical conflicts. The next phase of the clean tech revolution will be determined by how the world reacts to China's dominance, through competition, collaboration, or protectionism.
If you are looking for detailed and up-to-date China Export Data, You Can Contact Import Globals.
FAQs
Que. Why did China's clean tech exports to emerging markets surge in 2024?
Ans: Competitive pricing, massive production capacity, cutting-edge innovation, and strong demand for renewable technologies in emerging markets fueled the surge.
Que. Which sectors dominate China’s clean tech exports?
Ans: Solar PV products, wind turbines, lithium-ion batteries, electric vehicles, energy storage systems, and electric motorcycles/bicycles dominate the landscape.
Que. Which emerging markets were the largest importers of Chinese clean tech in 2024?
Ans: Brazil, Mexico, Pakistan, South Africa, and Indonesia were among the largest importers.
Que. What are the strategic risks of China's clean tech dominance?
Ans: Risks include potential overcapacity, market destabilization, trade disputes, and geopolitical tensions, particularly with the U.S. and EU.
Que. How do China's clean tech prices compare globally?
Ans: Manufacturing costs are 25-45% lower in China compared to India, the EU, and the U.S., making Chinese products highly competitive and more affordable internationally.
Que. Where to obtain detailed China Export Data?
Ans. Visit www.importglobals.com or email info@importglobals.com for more information on up-to-date China Export Data.
