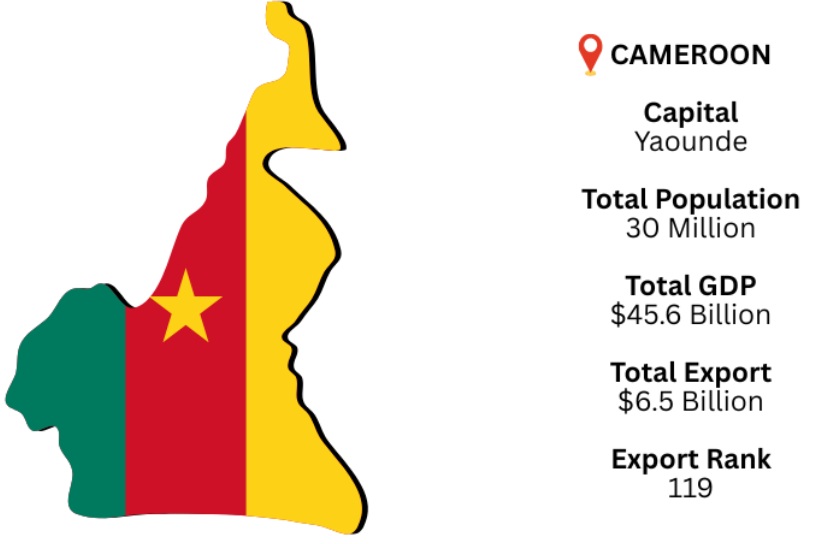
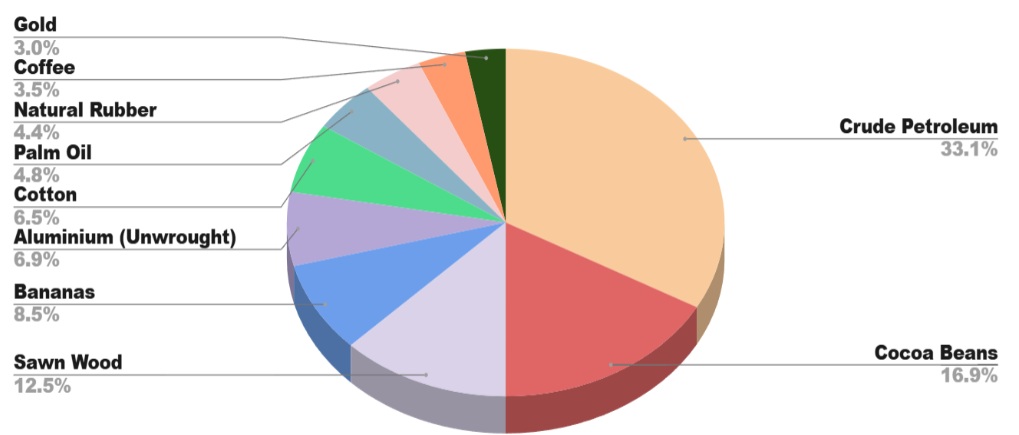
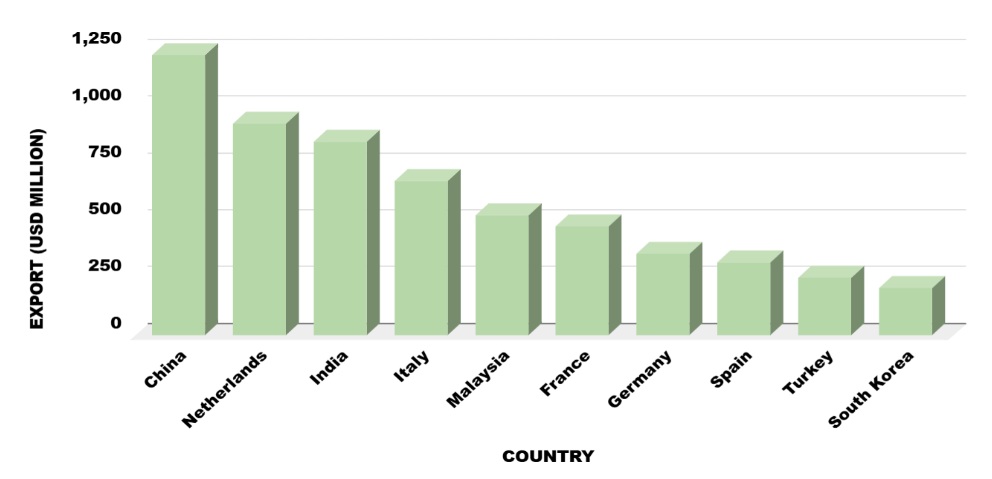
Nigeria, Chad, the Central African Republic, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, and the Republic of the Congo are the countries that border Cameroon, which is in Central Africa. Yaoundé is the capital, and Douala is the biggest port and commercial hub. As of 2024, Cameroon’s GDP is estimated at USD 45.6 billion. According to Cameroon export data, Cameroon is the 119th largest exporter in the world according to the global export landscape. The largest importer of Cameroonian commodities is China. In 2024, Cameroon's overall exports are expected to amount to USD 6.5 billion. Crude petroleum is the nation's top export and is essential to its economy.
Natural resource exports, such as wood, oil, and agricultural products, remain Cameroon's main source of income. The nation has established significant trading ties, particularly with European and Asian nations. Its export industry is essential to both employment generation and foreign exchange profits. Cameroon's standing in the international commercial environment has been enhanced by recent investments in port infrastructure, agro-processing, and energy.