
- Oct 22, 2025
Armenia's Global Trade: An in-depth Analysis for 2024–2025
The country's economy, which has a population of just under three million and no direct access to the sea, relies heavily on trade with other countries and links with other regions.
Armenia Import Data from Import Globals shows that Armenia has earned a reputation for itself in the global market, even if it has political and physical problems. By 2024, its total international trade had reached more than $30 billion, breaking a national record. This increase is due to many factors, including rising domestic demand, new re-export routes, and the company's entry into new markets, including China and the UAE.
A Look at Trade in 2024
In 2024, Armenia exported $13 billion worth of goods and imported $17 billion worth of goods. This shows that the country has a trade deficit, but it also shows that its economy is becoming more connected to global supply networks. The entire amount of trade was more than twice as large as it had been five years before, at almost $30.1 billion.
Armenia's Export Profile
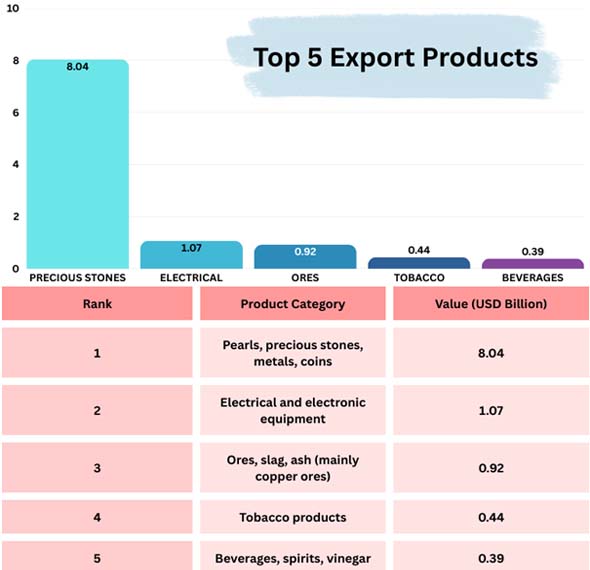
According to Import Globals' Armenia Export Data, Armenia's exports have changed a lot over the previous 10 years. New value drivers like electronics and precious metals have come along, but old ones like copper ores, textiles, and alcoholic beverages are still vital.
The Strength of Precious Metals
Jewelry, diamonds, and gold are among Armenia's most important exports. The country has become a processing and re-export powerhouse by using its own specialized refining talents and taking advantage of mismatches in global supply and demand. More than 21% of all shipments were gold.
Growth in Electronics
According to Import Globals' Armenia Import Export Trade Data, exports of electronic devices and communications equipment have expanded quickly. Some of this rise is due to changes in re-export tendencies, but it also shows how Armenia's economy is becoming more technology-driven.
Conventional Exports keep Value High
Even if precious metals and electronics are popular, copper ores and ferro-alloys are still needed. According to Armenia's import customs data, they help the mining sector in Armenia create more jobs and bring in more money from other nations. They are both a part of the country's culture and a good business.
Growth in Electronics
Exports of electronics and communications equipment have expanded quickly. Some of this rise might be explained by changes in the way Armenia's economy works, which is becoming more technology-driven.
Conventional Exports keep Value High
Even if precious metals and electronics are popular, copper ores and ferro-alloys are still needed. They help the mining industry in Armenia by creating jobs and bringing in more foreign currency. According to Armenia Import Trade Analysis, spirits, wines, and cigarettes are the country's vital merchandise in regional markets. These products are important for both cultural identity and business.
Medicines and Medical Tools
Most of the drugs and medical supplies that Armenia needs come from other countries, primarily Germany, India, and the United States. Even though this dependence is frequent in small economies, it shows how important strong supply chains are.
The main Places where Armenia Sells Things
Even if Armenia's exports go to many different places, there have been big developments in the last few years.
Russia: According to Import Globals' Russia Export Data, Russia has been the biggest export market for a long time, but its power is fading. In 2023, it will only account for 40% of exports.
United Arab Emirates (UAE): The UAE became Armenia's leading export destination in 2024, mostly because the gold and diamond industry was growing.
China and Hong Kong need a lot of electronics, re-exported goods, and Armenian ores.
Germany, Belgium, and the Netherlands are nevertheless steady buyers of Armenian goods, notably beverages and precious metals.
Georgia and Iraq: According to Import Globals' Georgia Import Data, regional neighbors are very significant for agricultural and food-based exports.
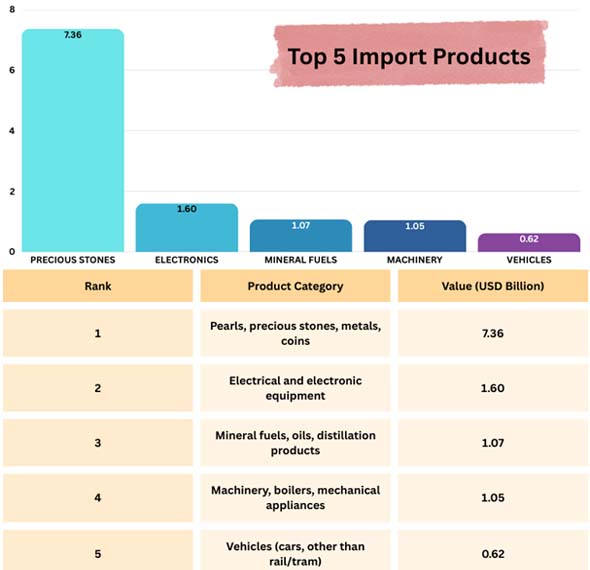
The main things that Armenia buys from other Countries
Armenia gets a lot of things from both its own markets and markets throughout the world.
Russia is still the major importer, bringing in energy, consumer goods, and equipment.
According to China Import Trade Statistics, Armenia's second-largest trading partner is China, which sends electronics, textiles, and cars.
Iran is a major buyer of building materials, agricultural goods, and petroleum gases.
Germany and the US are two of the most essential places to get technology, machinery, and medications.
Japan, Italy, Vietnam, and Turkey are all important but niche exporters of electronics, cars, and other specialized goods.
What the European Union does
According to Import Globals' Russia Import Data, the EU-Armenia Comprehensive and Enhanced Partnership Agreement (CEPA) has made it easier for businesses to enter the market and for rules to be the same across the board. The EU's trade share in Armenia is lower than that of the UAE or Russia, but it is nonetheless important since it gives access to high-quality, high-value markets. CEPA pushes for improvements in standards, customs, and openness, but the EU's need for Armenian metals, textiles, and spirits offers economic opportunities.
The Future of Armenia
Armenia's Potential as a Re-Export Hub: Import Globals' Armenia Import Export Trade Analysis says that Armenia is becoming more and more known as a place where electronics and precious metals may be traded between the Middle East and Eurasia.
ICT Integration: Armenia's growing IT sector might help the country become a digitally empowered business by linking services to real exports.
Branding for Agriculture: The markets in the Middle East and Europe for high-end agricultural commodities, including dried fruits, wines, and spirits from Armenia, are still growing.
Projects that Improve Connectivity: New trade routes through Georgia (to the Black Sea) and Iran (to Chabahar Port) can help businesses reach more people.
Problems with Trade in Armenia
Geopolitical Restrictions: Armenia can't choose its neighbors freely since its borders with Turkey and Azerbaijan are closed. This increases the cost of transportation greatly.
Dependency on Commodities: Changes in international pricing affect exports that depend largely on ores and precious metals.
Regulatory Scrutiny: Armenia Export Import Global Trade According to Data, Armenia's plans to re-export may be limited since the gold and diamond trade is attracting more attention throughout the world.
Trade Deficit: Relying on imports for a long time puts a strain on the external account.
In conclusion
The future of Armenia's commerce will depend on how well it balances its two roles as a hub for re-exports and a consumer-driven importer. It is expected that imports of cars, petroleum, and machinery will stay high in 2025, while exports of electronics and precious metals will stay strong. Policy help through CEPA, better logistics between Georgia and Iran, and stronger ties with China and the United Arab Emirates will all help the country go forward in the medium term. Import Globals is a leading data provider of Armenia import and export trade data. Sign up for Import Globals to learn more about commerce throughout the world!
FAQs
Que: What are the most crucial things that Armenia sells?
Ans. Armenia's main exports include gold, diamonds, jewelry, copper ores, ferro-alloys, spirits, and telecommunications equipment.
Que: What country does Armenia do the most business with?
Ans. Russia is Armenia's biggest source of imports, and the UAE became its biggest export market in 2024.
Que. Why does Armenia depend so much on imports?
Ans. Armenia is a small, landlocked country that doesn't have a lot of energy resources or industrial capabilities. It has to import cars, gasoline, machinery, and drugs.
Que. How significant is the EU to Armenia's trade?
Ans. The EU isn't Armenia's biggest trading partner by value, but it does offer high-value markets and regulatory support through the CEPA agreement. This helps Armenia deal with countries outside of its area.
Que. Where can you find complete Armenia Import Export Global Data?
Ans. For additional information on current statistics, go to www.importglobals.com or send an email to info@importglobals.com.
