
- Oct 23, 2025
German Industrial Production: Signs of Revival Amid Persistent Headwinds
Germany, the economic powerhouse of Europe, has a long history of being strong at creating things and engineering. But the manufacturers in the nation have been quite busy over the past two years.
Import Globals' Europe Import Data shows that production was affected by several factors, including rising energy costs, changes in international trade rules, problems in the supply chain, and low demand in the local market.
But something startling happened in May 2025 that offered everyone a little hope: German industrial production surged considerably, which meant that the economy could finally be getting better. This blog goes into detail on the recovery, the things that make the sector work, the problems that are at the heart of it all, and the larger effects on Germany's economy.
Key Points
In May, German businesses manufactured 1.2% more products than they did in April, when they lost a lot of goods, 1.6%. This was the first substantial advance in the market in months, and it was better than what analysts had predicted would happen. Import Globals' Germany export data says that exports went up by 1.0% from the year before. This is the greatest annual climb since early 2023, and it goes against a 2.1% decline in April.
The return is especially significant considering Germany's industrial sector had been progressively dropping since late 2022, and output levels were still around 6% lower than their peak before the recession. The rise in May shows that things are starting to get better, even though it doesn't make up for all the losses.
Factors in the Sector that are helping it Grow
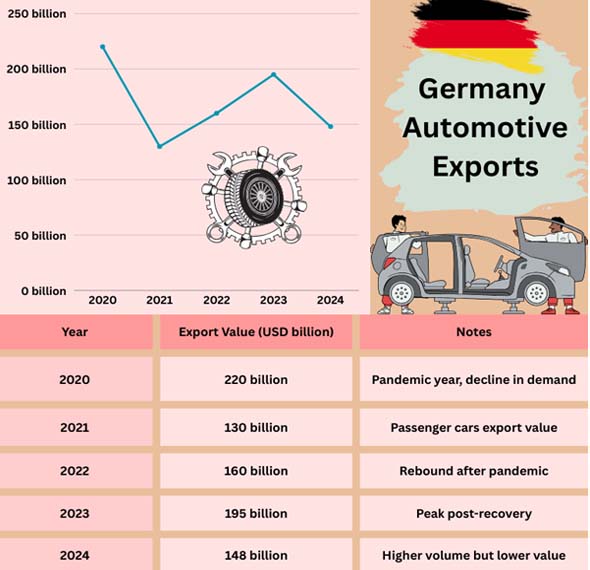
Making Cars
According to Import Globals' USA Import Data, Germany's famous automobile industry had the best performance, with a 4.9% gain in output in May. This jump was partly caused by U.S. importers buying more goods ahead in case tariffs go up. Germany is still the biggest exporter of cars in Europe, and the strength of the car sector is still a key part of the country's economy.
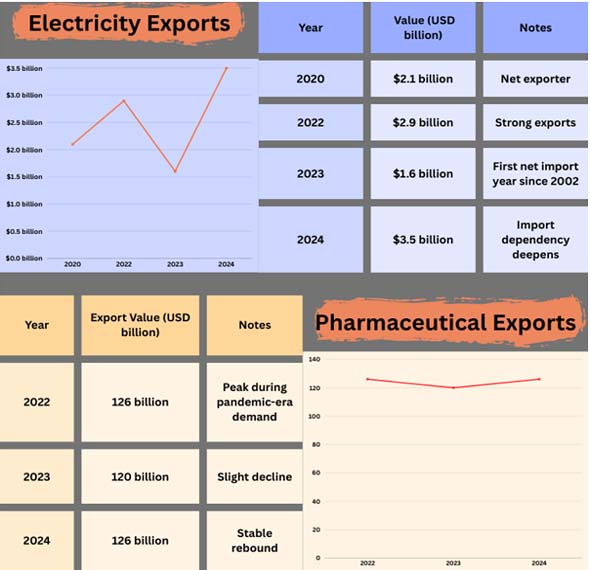
Making Drugs
The pharmaceutical industry did even better, with a 10% rise. The need for medical supplies throughout the world and the lack of tariffs on some pharmaceutical goods led to a surge in exports. According to Import Globals' Germany Import Data, Germany's well-established pharmaceutical industry is becoming a major source of growth, notably in the areas of biotechnology and specialty pharmaceuticals.
Making Energy
Energy output went up by 10.8% because there was more activity in household electricity and power generation. This spike not only boosted industrial output, but it also made energy-intensive industries like metals and chemicals stronger.
Industries that need a lot of Energy and Building
On the other hand, construction production fell by 3.9%, which is part of a long-term trend that has been going on because of high financing prices and low demand for real estate. According to Import Globals' Europe Import Trade Analysis, sectors that use a lot of energy, like chemicals and basic metals, also saw a 1.8% drop. This shows that high energy prices and structural problems are still putting pressure on these sectors.
Overall Trends and Results for Three Months
Industrial production went up 1.4% from the previous three months to the March–May three-month period. This flattening of the volatility shows that the return was part of a longer-term trend and not just a one-month outlier.
The order books portray a different tale, even while output has steadied. According to Import Globals' Germany Export Data, industrial orders declined by 1.4% in May. This was mostly because partners in the eurozone didn't want as many items. The things that were affected the worst were metals, capital goods, and electronics. This difference between orders and output shows how fragile the recovery is.
Basic Factors and Resilience
Tariff and Front-Loading Pressures
One of the main reasons May's outcome was so good was that exports were front-loaded. As Americans expected 25% tariffs on European autos and other goods, orders from Germany went up. This provides a short-term boost, but once tariffs are fully in place, it raises questions about how long it will last.
Help from the Government
Berlin has suggested a number of tax reductions and investment incentives in order to make businesses more competitive. According to Import Globals' Europe Import Data, spending more on infrastructure, such as public works and defense improvements, will probably lead to higher demand in essential sectors. These steps, together with the European Central Bank's reduced interest rates, may help keep things moving.
Strong exports despite weak conditions at Home
Germany's resurgence is now being driven by exports. But demand at home remains poor, especially for consumer goods and construction. For industrial production to keep increasing, people in the eurozone will need to spend more money and want more things.
Problems and Risks Ahead
Pressures on Costs and Energy
As per Germany Import Shipment Data, even if energy prices have dropped from their 2022 highs, they are still higher than they were before the crisis. The prolonged lag of energy-intensive industries is hurting overall performance. Germany is still working toward renewable energy, but it will take time and a lot of money to get all the benefits.
More trade and a Stronger Euro
According to Europe Import Trade Statistics from Import Globals, a stronger euro makes things harder by making German goods more expensive on overseas marketplaces. If the currency keeps getting stronger as compared to the dollar and other major currencies, it might hurt GDP and exports.
Issues of transportation and supply chain Network
Presently, the Rhine and other big rivers have lower water levels because of the very dry summer. This has made it difficult to move goods inland and increase the cost of doing business. Because waterways transportation is important for industrial goods and raw materials. These limitations are making the cost limits even stricter.
Problems with the structure
According to Germany Export Import Global Trade Data, Germany's industrial production is still far behind its peak before 2022, even if it went up in May. The corporation still has a lot of fundamental problems, such as aging workforce, challenges adjusting to energy-intensive fields, and reliance on demand from other sources.
Prospects: A Weak Return
Germany's industrial sector is at a crossroads. On the other hand, the May rebound demonstrates that big companies like energy, pharmaceuticals, and cars are performing well. The rally won't continue long, though, unless the economy gets a lot better. People are apprehensive about trade tensions, rising expenses, and sluggish demand at home, which is why this is happening.
If the government can get more people to invest, get rid of barriers, and keep export demand high, Germany's industrial sector could slowly start to come back to life. However, businesses and governments need to be ready for changes since global commerce is unpredictable and there are problems with energy. Import Globals is a leading data provider of Germany import export trade data. Join Import Globals to learn more about trade throughout the world!
FAQs
Que: How much did Germany's industrial production expand in May 2025?
Ans. It rose by 1.0% from one year to the next and 1.2% from one month to the next, which was the reverse of what happened in April.
Que. What industries helped the economy bounce back the most?
Ans. According to Germany Import Export Trade Analysis, automobiles (+4.9%), pharmaceuticals (+10%), and energy (+10.8%) were the main drivers of growth, making up for losses in construction and industries that use a lot of energy.
Que. What are the major threats to Germany's industrial sector in Q3?
Ans. Some of the biggest challenges include weak demand in the domestic market, tariffs, high energy prices, a stronger euro, and issues with the structure of heavy industries.
Que: Will the recovery process last?
Ans. The May rebound is good news, but it's mostly due of short-term problems like front-loading exports. For long-term success, there has to be ongoing worldwide trade, changes to the way things are set up, and more demand in the local area.
Que. Where can you get additional information about Germany Import Export Global Data?
Ans. For additional information on current statistics, go to www.importglobals.com or send an email to info@importglobals.com.
