
- Jan 14, 2026
Germany's Most Important Trade Partners: the EU, the US, China, and More (2025–26)
It exports high-quality commodities such cars, machinery, chemicals and medicines, and electrical equipment. It also has a wide network of suppliers and customers around the world.
Three major factors will affect Germany's trade with other countries in 2025–26: (1) demand cycles in Europe and North America; (2) strategic de-risking and industrial policy, especially when it comes to China; and (3) tariffs, compliance, and supply-chain resilience that are changing where companies buy parts and where they sell finished goods.
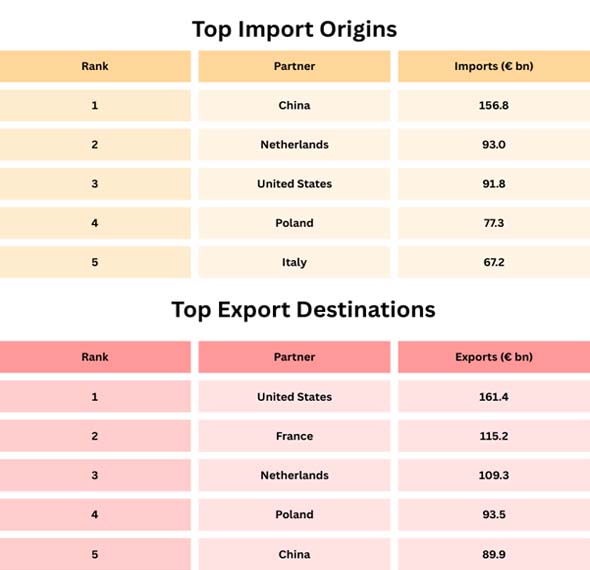
As per Germany Import Data by Import Globals, it's clear that the EU is still Germany's most important trading partner. The US and China are the two most important countries outside the EU that can influence the headline numbers, especially when tariffs, currency changes, or slowdowns in industry happen.
The Big Picture: Why Partnerships Will Be More Important in 2025–26
Germany's "key partners" are not merely clients; they are often also co-producers. A gearbox may come from one EU country, be put together with a machine in Germany, and then be sent to another EU market or the U.S. This is why it's preferable to think of Germany's trade map as a network:
- EU Partners: As per Germany Import Trade Analysis by Import Globals, deep supply chains, less friction, and a lot of volume.
- United States: significant demand for capital goods, cars, chemicals, and pharmaceuticals, which is also a substantial source of export revenue.
- China is a huge source of intermediate goods and a key sales market for some German companies. It is also a strategic risk topic.
- Beyond (the UK, Switzerland, Turkey, India, the Gulf, ASEAN, Mexico, etc.): markets for diversification, growth in specialist markets, and paths for balancing risk.
Partnership 1: The EU and Germany's Industrial Home Market
The EU is Germany's biggest and most dependable place to do business because it has a lot of businesses and minimal obstacles to entry. Germany's biggest partners are France, the Netherlands, Poland, Italy, Austria, Belgium, and Czechia. As per Germany Exporter Data by Import Globals, these countries are all strongly involved in common manufacturing systems:
- France is an important end market and an industrial partner (in the automotive, aerospace, chemicals, and consumer goods industries).
- The Netherlands is an important commercial center. The enormous numbers show that there is real demand and that Dutch ports and logistics play a big role in moving European goods.
- Poland and Czechia are very important for manufacturing supply chains, such as those for parts, industrial assembly, and automotive networks.
- Italy, Austria, and Belgium all promote commerce in machinery, chemicals, specialized manufacturing, and intermediate inputs going both ways.
- The EU partnership in 2025–26 is less about "new market entry" and more about competitiveness and capacity. Energy costs, industrial subsidies, emissions laws, and cross-border investment decisions all affect where production stays in Europe, moves inside Europe, or moves outside of Europe.
Partnership 2: The US is Germany's Most Important Customer
Germany's top export market by value is the U.S. This is because Americans want a lot of high-end machinery and industrial equipment, cars and high-end auto parts, chemicals/pharmaceuticals and precision goods, and engineering-intensive products where Germany's brand and quality give them pricing power.
But the U.S. relationship has been increasingly sensitive to policy changes since 2025–26. Tariff regulations and political instability can rapidly hinder the inflow of orders, particularly within the automobile and industrial products sectors. As per Germany Importer Data by Import Globals, trade data from late 2025 shows that the swift pace of this sudden transformation in a single month, and shipments to the United States experienced a significant decline in trade as compared to the previous year. This illustrates how swiftly policy changes can jeopardize a robust business relationship.
As per Germany Import Data by Import Globals, Germany's customary strategic approach is not to withdraw from the U.S. market, considering its importance, but rather to diversify its product portfolio into more resilient sectors such as pharmaceuticals and specialized machinery, to expand its local manufacturing footprint where possible, and to mitigate tariff exposure by restructuring its supply chain.
China does two things at the same time:
- A big provider to Germany (the biggest source of imports in 2024).
- A very important place for German exports (one of the top five markets).
This makes it hard to find a balance. German industry gets a lot of its electronics, mechanical parts, consumer goods, and intermediate items from China. It also requires Chinese demand in a few areas. As per Germany Export Data by Import Globals, businesses and politicians are also paying more attention to "de-risking," which involves avoiding getting too much strategic information from one source.
In 2025–26, the relationship with China is affected by: price competition and import pressure in some industries; worries about the security of supplies of important goods; changing Chinese domestic demand (especially for some capital goods); and the global political climate affecting trade rules and technology flows.
Quick changes can potentially modify the order of partners. As per Germany Import Trade Statistics by Import Globals, trade data for different parts of 2025 showed that China will become Germany's biggest trading partner by turnover, taking over from the U.S. This shows how quickly the ranking can change when commerce, rules, and policies change.
Partnership 3: China—A Strong Supplier and a Complicated Demand Story
The UK is a big, high-value market outside of the EU.
The UK is still one of the best places to send goods. After Brexit, there has been more demand for documentation, compliance, and supply-chain planning. As per Germany Import Shipment Data by Import Globals, sectors like equipment, chemicals, cars, and medical products will still be important in 2025–26.
Switzerland: High demand for high-income goods and specialized two-way commerce
Switzerland is always one of Germany's best partners. Pharmaceuticals, chemicals, precision instruments, machinery, and high-value intermediate commodities are some of the most common things that are traded.
As per Germany Export Import Global Trade Data by Import Globals, Turkey, the Gulf markets, India, ASEAN, and Mexico: Targeted growth paths. Turkey connects Europe's manufacturing periphery with big domestic demand and production networks. This is important for diversification.
Gulf markets can be big buyers of high-end industrial items and infrastructure-related purchases. People are talking more and more about India as a strategic partner for growth and diversity. ASEAN and Mexico are important for moving factories, automotive supply chains, and finding new ways to get goods.
In 2025–26, "beyond" markets are less about replacing the EU/U.S./China triangle and more about lowering concentration risk and finding development in places where industrial policy and demographics are good.
The UK, Switzerland, and the "Diversification Belt" are not the only places.
What to Look for in 2025–26: The Useful Signs
1) The EU's Industrial Growth
As per Germany Import Export Trade Analysis by Import Globals, Germany suffers the effects of a slowdown in EU industrial activity very away because the EU is its main client and supplier.
2) Rules for Tariffs and Compliance
Tariffs (especially those linked to the U.S.) and regulatory requirements can shift trade flows faster than changes in demand do.
3) How much China Imports Compared to how much it De-Risks
Keep an eye on whether imports from China stay high or whether "China+1" sourcing from ASEAN, India, Mexico, and Eastern Europe picks up speed.
4) Moving between Sectors
Cars and machines might be cyclical, while medicines and drugs and other specialized equipment can be more stable. When demand in a sector changes, partner rankings change too.
Conclusion
As per Germany Import Export Trade Data by Import Globals, the EU will continue be Germany's most important trading partner in 2025–26. The U.S. will buy the most goods from Germany, and China will be the main supplier of imports and a big (but hard) market for exports. The "beyond" category, which includes the UK, Switzerland, and markets that are rising quickly or are important for strategic reasons, is becoming more and more important for diversification. Germany's economy depends on keeping this relationship portfolio strong since changes in government can have a bigger influence on business than changes in consumer demand. This means that the EU will be more connected, it will be safe to travel to the U.S., China will know how to handle risks, and the EU will only grow in certain sectors. Import Globals is a leading data provider of Germany Import Export Trade Data.
FAQs
Que. Who does Germany do the most business with?
Ans. In 2024, the US was Germany's top trading partner in terms of overall goods trade, and China was the biggest supplier of imports.
Que. Why is Germany's most significant trade area still the EU?
Ans. Germany's production system is connected to supply chains all throughout Europe, and trade between EU countries is both large and easy.
Que. Is Germany less reliant on China for trade in 2025–26?
Ans. The fundamental goal of the plan is to "de-risk," although China is still the main supplier. The speed of change depends on costs, the availability of other options, and industrial policy.
Que. What other markets are important besides the EU, U.S., and China?
Ans. The UK and Switzerland are still crucial high-value partners. Turkey, India, the Gulf markets, ASEAN, and Mexico are all seen as vital places to diversify.
Que. Where to get detailed Germany Import Export Global Data?
Ans. Visit www.importglobals.com.
