
- Jul 02, 2025
Mexico’s Automotive Export Industry: A Comprehensive Overview
Mexico has emerged as a key hub for the production and export of passenger cars, trucks, and automotive parts by utilizing its advantageous geographic location, highly skilled labor population, and solid trade relations, particularly under the USMCA agreement. With major international automakers like General Motors, Ford, Nissan, and Volkswagen operating large-scale plants throughout the nation, the automotive sector not only propels Mexico's export economy but also significantly contributes to employment and GDP, according to Mexico Import Custom Data by Import Globals.
General Economy
Mexico, which ranks 15th in the world by nominal GDP, has one of the biggest and most vibrant economies in Latin America. Manufacturing, services, agriculture, and exports all make major contributions to its diverse economic structure. With a lengthy border with its biggest commercial partner, the United States, the nation enjoys an advantageous geographic location. Mexico has signed several trade agreements over the years, including the United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA), which has allowed it to become a crucial component of global supply chains, particularly in the automotive, electronics, and aerospace industries, according to a report by Import Globals on Mexico Import Trade Analysis.
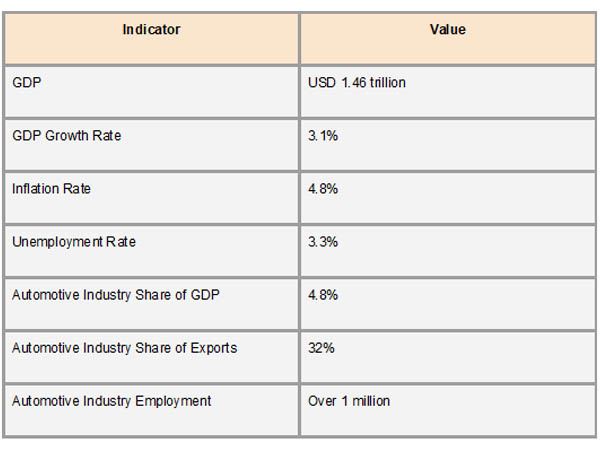
Mexico's economy is robust despite obstacles like inflation, volatile oil prices, and sporadic political unpredictability. According to research on Mexico Export Data Published by Import Globals, the country's GDP was estimated to be $1.46 trillion, growing at a stable 3.1% annual rate. The rate of unemployment stayed low at 3.3%, and important industries, especially manufacturing, continued to receive foreign direct investment. To draw in multinational corporations and strengthen its standing as a top export-oriented economy, the Mexican government has also made investments in industrial parks and infrastructure development.
Mexico's Automotive Export Data
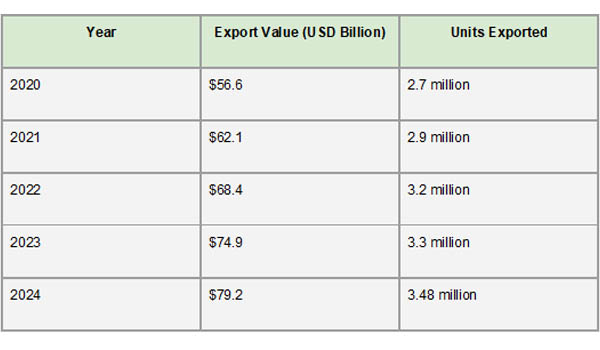
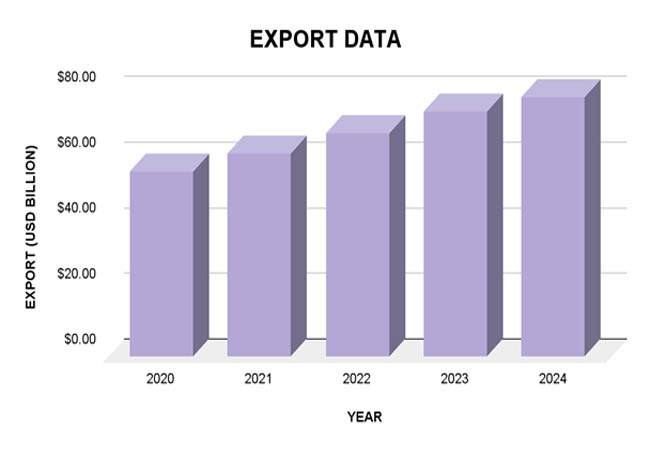
Over the last five years, Mexico's automotive export industry has grown and remained resilient, solidifying its place as one of the world's leading auto exporters. According to Import Globals' Mexico Import Data, the value of automobile exports rose from $56.6 billion to an expected $79.2 billion between 2020 and 2024. Due to increased global demand and reestablished supply chain stability, output and exports have recovered from the pandemic-induced downturn in 2020, as seen by this growth. During this time, the number of automobiles exported also increased substantially, reaching over 3.48 million in 2024. Increased demand in North American and European markets, as well as strategic expansions by international automakers operating in Mexico, are mostly responsible for this growth.
Nearly 80% of Mexico's automobile exports go to the United States, making it the country's top export destination. Canada, Germany, Brazil, and Colombia are other noteworthy markets, according to Import Globals' Mexico Import Trade Statistics. Both a strength and a risk, Mexico's strong reliance on the U.S. market exposes it to changes in trade policy and tariffs while simultaneously guaranteeing high-volume exports. Nonetheless, the nation remains a desirable location for the production and export of automobiles due to its extensive trade agreements, affordable workforce, and effective logistics system. Mexico is the fourth-largest exporter of automobiles in the world as of 2024, after China, Japan, and Germany.
Major Export Destinations
Nearly 80% of all cars made for export in 2024 will go to the US, making it by far the biggest market for Mexican auto exports. This supremacy is supported by proximity, smooth trade under the USMCA agreement, and the intricately linked supply chains between Mexican and American automakers, according to Mexico Import Shipment Data From Import Globals. In addition to having production facilities in Mexico, well-known American automakers like Ford and GM also mostly depend on Mexican assembly lines and parts for their North American operations. Mexico contributes to the total volume of trade by exporting a sizable amount of car parts and components to the United States in addition to fully built automobiles.
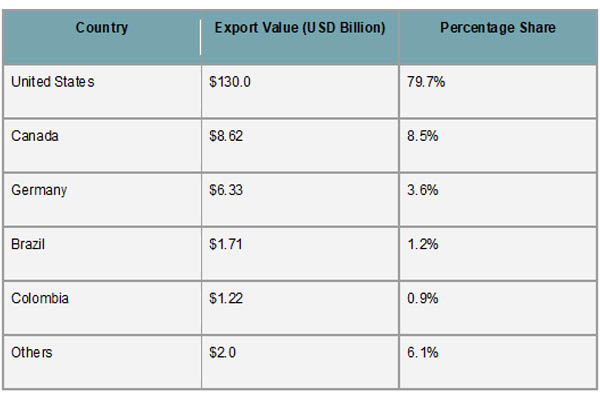
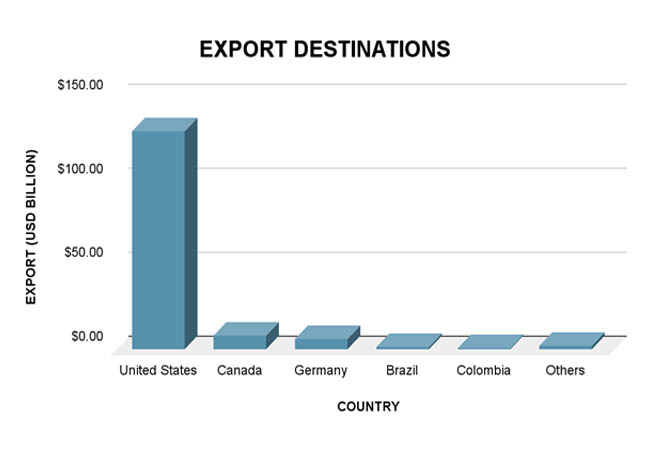
Mexico now sells automobiles to countries outside of the US, including Canada, Germany, Brazil, and Colombia. Germany leads among non-American partners because of its robust automotive industry and demand for particular car types, while Canada, a member of the USMCA, is the second-largest destination. Latin American nations like Brazil and Colombia are also important markets, according to Import Globals' Mexico Import Export Trade Analysis, which reflects Mexico's attempts to diversify its automotive trading portfolio. These key locations help Mexico reduce the risks of being overly dependent on one market and sustain steady demand for its automobile exports despite changes in the world economy.
Major Automotive Production Regions in Mexico
The main centers of automotive production in Mexico are positioned in the country's north and center, providing manufacturers with easy access to trained labor, effective logistics, and proximity to the U.S. border. One of the most well-known car routes is the Bajío region, which consists of the states of Guanajuato, Querétaro, and San Luis Potosí. Major facilities for businesses like General Motors, Mazda, Honda, and BMW are located in this region, per a report by Import Globals on Mexico Export Import Global Trade Data. Another important automotive cluster is Puebla, which is home to Audi's advanced production line and Volkswagen's biggest facility outside of Germany. These areas gain from strong government assistance, advanced industrial infrastructure, and intimate connections to international supply networks.
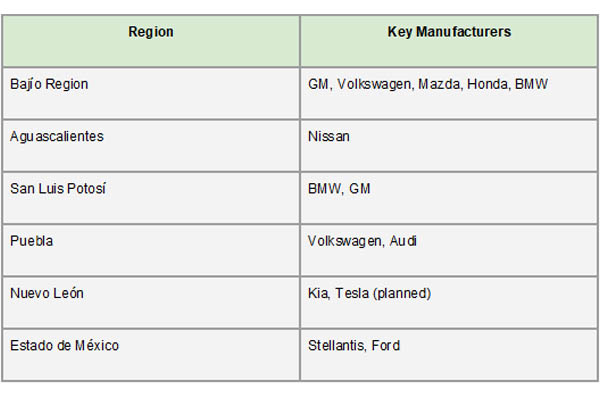
States like Coahuila and Nuevo León are growing in significance in northern Mexico because of their proximity to the U.S. market. Particularly, Tesla's planned "Gigafactory" and Kia's current production facilities are drawing attention to Nuevo León. Another important state is Aguascalientes, which is well-known for its long-standing alliance with Nissan, which runs one of its most efficient facilities there. According to Import Globals' Mexico Import Export Global Data, the Estado de México, which is home to important Ford and Stellantis facilities, also plays a significant role. These areas work together to provide a strong manufacturing foundation that supports Mexico's position as a top exporter of automobiles.
Product Analysis
The Harmonized System (HS) Code 8703, which applies to automobiles and other motor vehicles principally intended for human transportation, is Mexico's main export. Mexico exports a wide variety of automobiles, including pickup trucks, SUVs, compact cars, and a rising number of electric and hybrid models, according to Mexico Import Export Trade Data. The Nissan Versa, Volkswagen Jetta, Chevrolet Silverado, Toyota Tacoma, and Ford Bronco are some of the most popular vehicles that are exported. In addition to being put together in Mexico, these cars are frequently produced using a large proportion of locally obtained components, which raises the value-added component of the exports.
Cars and other motor vehicles principally used for passenger transportation (HS Code: 8703). The Nissan Versa, Ford Fusion, Volkswagen Jetta, Toyota Tacoma, and Chevrolet Silverado are the top export models. Vehicle Types are electric vehicles, pickup trucks, SUVs, and passenger automobiles.
According to Import Globals' Mexico Import Data, manufacturing strengths include a strong supply chain, affordable labor, proximity to the U.S. market, and advantageous trade agreements. A developed supply chain network, affordable and skilled labor, and proximity to important markets are the main reasons why Mexican automobiles are competitive. By utilizing free trade agreements and cutting-edge manufacturing technologies, numerous international automakers have included Mexico in their North American operations. According to Import Globals' Mexico Import Custom Data, investments in EV assembly lines and battery manufacturing are helping to progressively shape the trend toward electric vehicles. Mexico's automobile exports continue to be relevant and competitive due to its capacity to adjust to global trends, uphold constant quality standards, and satisfy the unique requirements of foreign markets.
Global Automotive Exporters
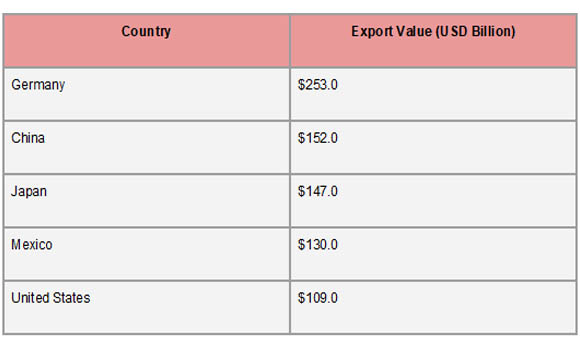
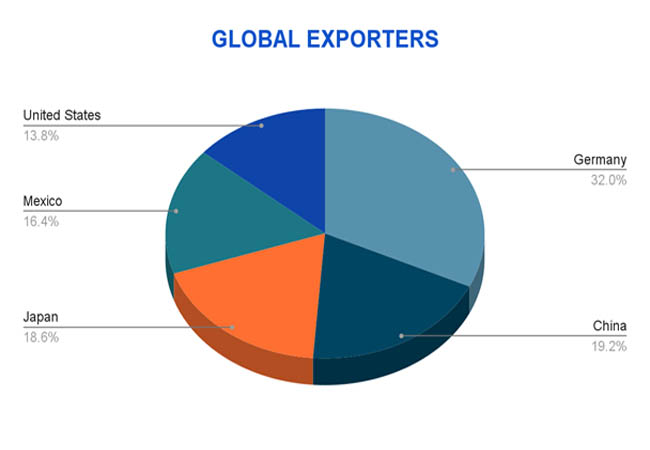
A small number of industrial giants control the majority of the global automobile export industry, with the US, Japan, and Germany at the forefront. Known for its luxury brands like BMW, Mercedes-Benz, and Volkswagen, Germany remains the leading automobile exporter in the world by value. According to Import Globals' Mexico Import Export Trade Analysis, Germany exported cars valued at about $155.4 billion. Driven by the desire for dependable, fuel-efficient brands like Toyota, Honda, and Nissan worldwide, Japan comes in second with $98.1 billion. Third place goes to the United States, which exports about $85.7 billion worth of automobiles, mostly to China, Canada, and Mexico. These nations profit from well-established automotive sectors, substantial R&D expenditures, and well-known international brands.
Mexico has quickly risen through the rankings to become the fourth-largest exporter of automobiles, with an expected 2024 export value of $79.2 billion. Its function as a production center for international brands rather than domestic OEMs drives its performance. According to Import Globals' Mexico Export Import Global Trade Data, South Korea, Canada, and the United Kingdom each contribute between $30 and $50 billion a year, making them major players in the global car export sector. Mexico is a key player in the global automotive supply chain because of its strength in mass production and strategic trade partnerships, especially with North America. In contrast, European nations prioritize innovation and premium quality, while Asian exporters prioritize efficiency and affordability.
Forecast Trends and Strategic Implications of Trade Agreements
Mexico's automobile exports have benefited from the United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA), which grants them tariff-free access to North American markets.
Foreign Investment: Businesses like BYD are looking into manufacturing prospects in Mexico, according to Mexico Export Data From Import Globals, demonstrating trust in the nation's automotive industry.
Challenges: Manufacturers are reevaluating their plans as a result of the uncertainty brought up by recent U.S. tariffs on automobile imports.
Forecast: Despite obstacles, it is anticipated that Mexico's automobile exports would rise due to smart investments and rising worldwide demand.
Forecasts show that Mexico's automotive export industry is expected to continue growing due to a growing shift toward electric vehicle (EV) production, nearshoring, and rising global demand. A robust foundation for sustained export growth is offered by trade accords like the USMCA, the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP), and Mexico's free trade agreements with more than 50 nations. Through these accords, Mexico is positioned as a crucial center in global automotive supply chains by lowering tariffs, streamlining logistics, and promoting foreign direct investment. By accessing European and Latin American markets, they strategically allow Mexico to draw in EV production, improve its competitiveness against Asian exporters, and lessen its over-reliance on the United States.
Overview of Prices
Each vehicle's average export price is about USD 22,700.
Elements That Affect Prices:
- Labor expenses
- Prices of raw materials
- Rates of exchange
- Trade policies and tariffs
With typical unit export costs ranging from $12,000 to $25,000, the cost of Mexico's exported cars varies greatly depending on the type, brand, and market destination. SUVs, pickups, and luxury vehicles built in Mexico, like the Audi Q5 or Ford Bronco, command higher export prices than economy and compact sedans, like the Nissan Versa or Chevrolet Aveo. Rising input prices, the move to electric and hybrid vehicles, and inflationary pressures in international markets have all contributed to recent patterns that indicate a slow price growth. However, Mexico's low production costs, effective labor, and advantageous trade agreements—which provide tariff-free exports to important automotive markets like the U.S., Canada, and the EU—allow it to maintain a competitive pricing edge.
In conclusion
Mexico's industrial capabilities and strategic trade positioning are demonstrated by its automobile sector. A study by Import Globals on Mexico Import Export Trade Data states that Mexico is well-positioned to maintain its position as a top exporter of automobiles due to its strong infrastructure, highly qualified workforce, and advantageous trade agreements. But for long-term prosperity, managing the dynamics of international trade and adjusting to new obstacles will be essential.
If you are looking for detailed and up-to-date Mexico Export Data, You Can Contact Import Globals.
FAQs
Que: What is the main export from Mexico?
Ans: Mexico's top exports are automobiles, including passenger cars and auto parts.
Que: Which nation is Mexico's top export destination for automobiles?
Ans: The US, which will make up about 79.7% of exports in 2024.
Que: Which Mexican regions are the main producers of automobiles?
Ans: State of Mexico, Puebla, Aguascalientes, San Luis Potosí, Bajío Region, and
Que: What effects have recent U.S. tariffs had on Mexico's car sector?
Ans: Because of the uncertainty created by the 25% tariffs, manufacturers are reassessing their export and production plans.
Que. Where to obtain detailed Mexico Export Data?
Ans. Visit www.importglobals.com or email info@importglobals.com for more information on up-to-date Mexico Export Data.
