
- Jul 07, 2025
Nicaragua Import Data & Economic Overview
The largest nation in Central America, Nicaragua, has demonstrated remarkable economic resilience in recent years thanks to higher remittance inflows, export-oriented industry, and better macroeconomic stability. Nicaragua has maintained consistent economic growth through efficient governmental measures and outside assistance, according to Nicaragua Import Export Trade Data by Import Globals, despite global obstacles like inflationary pressures and supply chain disruptions. Agriculture, textiles, services, and light manufacturing are the main drivers of the nation's diverse economy, which has led to its growing integration into international trade networks.
Because they meet the rising demand for gasoline, machinery, pharmaceuticals, and raw materials for industrial growth, imports are essential to Nicaragua's development. A research from Import Globals on Nicaragua Import Custom Data claims that the country's trade prospects have been improved by its advantageous geographic location and membership in trade accords like CAFTA-DR (Dominican Republic–Central America Free Trade Agreement). Examining Nicaragua's import statistics from 2020 to 2024, as well as its trading partners and import product categories, provides important information about the nation's industrial priorities, economic reliance, and prospects for growth.
Indicators of the Nicaraguan Economy
The rise of the services sector, especially in the hotel, restaurant, and retail industries, has been the main driver of Nicaragua's economy's recent moderate growth, with a GDP growth rate of 4.6% in 2023. But according to Import Globals' Nicaragua Import Trade Analysis, growth decreased to 3.6% in 2024 as a result of lower output in industries like manufacturing, agriculture, livestock, and fisheries. To maintain economic stability, remittances have been crucial in boosting private consumption. In the second half of 2023, the employment rate was 66.9%, which was nearly at pre-pandemic levels. By June 2024, the employment rate for women had risen to 54.9%. Estimates show that poverty rates have decreased, falling from 13.1% in 2022 to 12.5% in 2023.
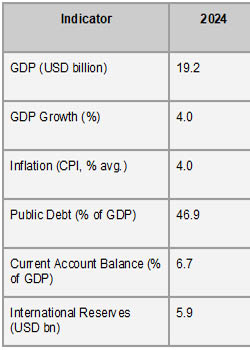
With the help of a crawling peg exchange rate system, fairly restrictive policy rates, and falling global prices, inflation has been on the decline, half from 5.6% in 2023 to 2.8% in 2024. Because of sound macroeconomic and fiscal measures, the public debt has also declined, from 49.6% of GDP in 2023 to an anticipated 47.1% in 2024. Despite these encouraging signs, Nicaragua is vulnerable to negative risks, such as natural disasters, fluctuations in food and oil prices, economic downturns in important trading partners, and tighter financial conditions that could disrupt trade and external flows and result in inflation, increased unemployment, and difficulties refinancing public debt, according to Nicaragua Export Data by Import Globals.
Import Data of Nicaragua
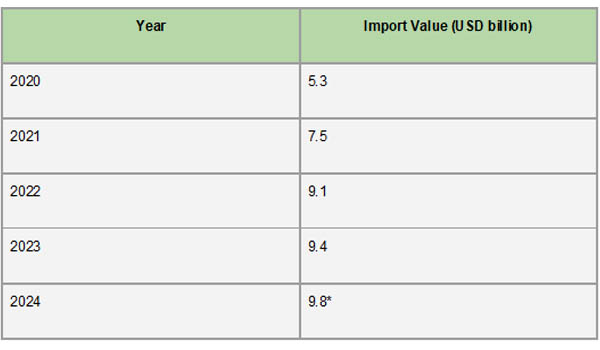
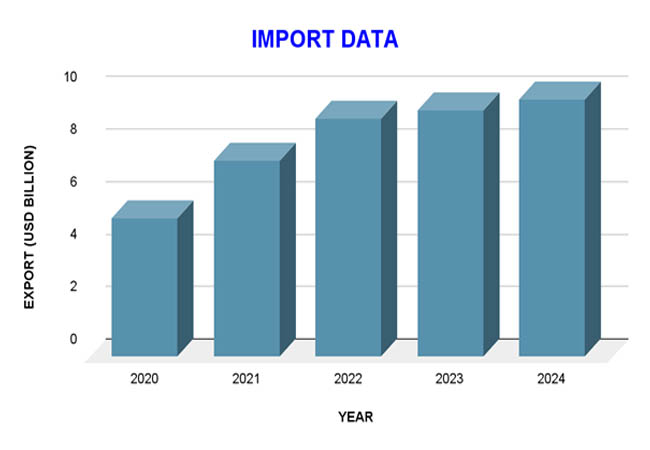
Nicaragua's import landscape expanded significantly between 2020 and 2023, a reflection of the nation's economic recovery and rising consumer demand. About $5.96 billion was spent on imports in 2020; this amount increased to $8.5 billion in 2021 and $10.25 billion in 2022. In 2023, imports reached $10.53 billion, a significant increase over the previous four years. According to Nicaragua Import Data From Import Globals, this increasing trend highlights the nation's growing consumer demand and industrial activity, which calls for a wide variety of imported items to support different economic sectors.
A dependence on particular product categories is seen in the makeup of Nicaragua's imports. With a value of $1.54 billion in 2023, mineral fuels and oils were the largest import category, underscoring the nation's reliance on energy imports. Electrical and electronic equipment, which is necessary for both industrial and consumer purposes, came next with imports totaling $854 million, according to Nicaragua Import Trade Statistics by Import Globals. $720 million was spent on cars and auto parts, which reflected the demands of the transportation industry. Plastics, machinery, clothing, and pharmaceuticals were other important import sectors that fueled the nation's consumer and industrial industries.
Major Import Partners Of Nicaragua
A small number of nations controlled the majority of Nicaragua's imports in 2023, which was indicative of the country's strategic trading partnerships and regional economic integration. The largest import partner was the United States, which contributed items worth about $2.7 billion, or 24% of Nicaragua's total imports. According to Import Globals' Nicaragua Import Shipment Data, China came in second with $1.38 billion in shipments to Nicaragua, or 12.6% of the import share. Another important partner was Mexico, which contributed $1.02 billion worth of goods, or 9.35% of imports. Together, these top three partners were responsible for about half of Nicaragua's import volume, highlighting their crucial importance in the dynamics of the nation's commerce.
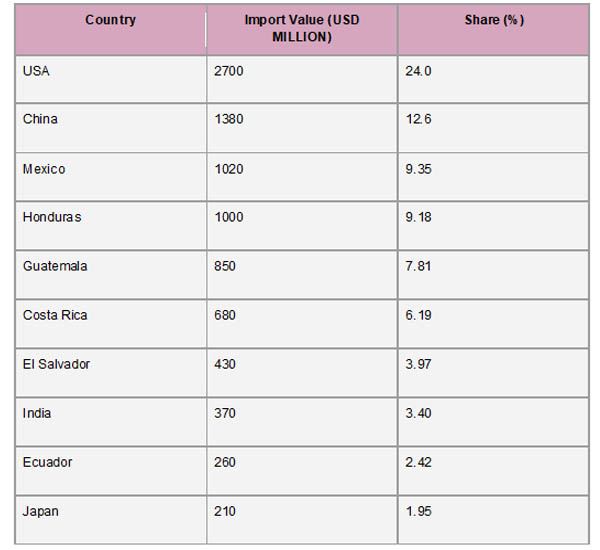
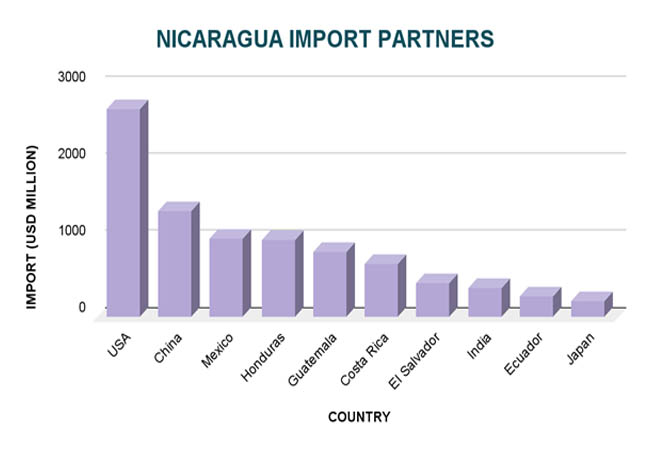
In addition, Nicaragua's import activities were significantly influenced by its neighbors in the region. According to Import Globals' Nicaragua Import Export Trade Analysis, Honduras contributed $1 billion (9.18%) worth of goods, while Guatemala exported $852 million (7.81%). El Salvador provided $433 million (3.97%) and Costa Rica $675 million (6.19%). India also played a significant role, sending $371 million (3.4%) worth of commodities to Nicaragua. These numbers demonstrate how important regional and global collaborations are to meeting Nicaragua's import requirements in industries including electronics, textiles, machinery, and pharmaceuticals.
Major Product Categories of Nicaragua Imports
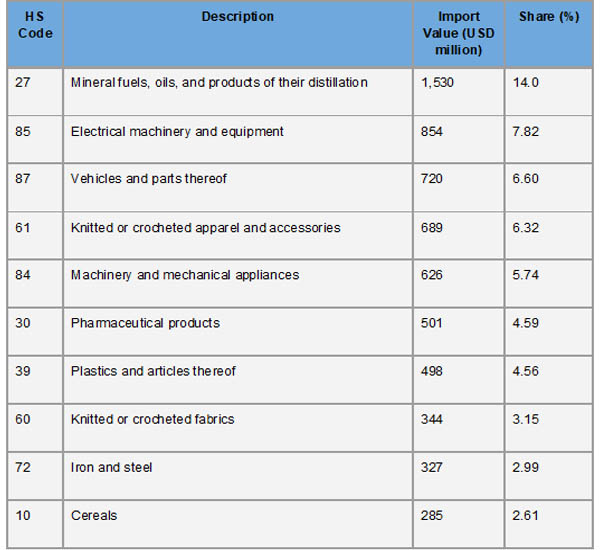
As a result of Nicaragua's reliance on imported energy sources, mineral fuels and oils (HS Code 27) accounted for the largest portion of its import portfolio in 2023, totaling around $1.54 billion. Electrical machinery and equipment (HS Code 85), which is necessary for both industrial operations and consumer demands, came next with imports worth $854 million, according to Nicaragua Export Import Global Trade Data by IMPORT GLOBALS. The $720 million in vehicles and automotive parts (HS Code 87) indicates growth in the logistics and transportation industries. To promote the domestic textile and apparel industry, $690 million worth of knitted and crocheted apparel and accessories (HS Code 61) were imported. Imports of machinery and mechanical appliances (HS Code 84) totaled $627 million, highlighting continuous industrialization initiatives.
The significance of healthcare and medical goods was highlighted by the $501 million in imports of pharmaceutical products (HS Code 30). According to Import Globals' Nicaragua Import Export Global Data, $498 million worth of plastics and their articles (HS Code 39) were imported to meet a range of manufacturing and packaging requirements. $344 million was spent on knitted or crocheted materials (HS Code 60), which are vital to the textile industry. Imports of iron and steel (HS Code 72), which are essential for building and infrastructure projects, totaled $327 million. In line with the nation's food security plans, $286 million worth of cereals (HS Code 10) were imported.
Strategic Implications
Energy Dependency: Nicaragua's heavy reliance on foreign energy sources is highlighted by the substantial import of mineral fuels, underscoring the necessity of making investments in renewable energy to improve energy security.
Industrial Development: Machinery and electrical equipment imports show continuous industrialization activities, indicating prospects for the expansion of domestic industry, according to Nicaragua Export Data by Import Globals.
Healthcare Sector: The need for healthcare services and the possibility of expanding domestic pharmaceutical production are reflected in the importation of pharmaceutical items.
Textile Industry: The significant imports of clothing and textiles indicate a thriving textile sector that offers prospects for value addition and vertical integration.
Strategic dependencies that directly affect Nicaragua's development strategy and economic resilience are revealed by its import trends. The significant dependence on mineral fuels emphasizes how urgent it is to diversify energy sources, particularly by investing in renewable energy, to improve energy security. According to Import Globals' Nicaragua Import Data,the substantial imports of automobiles, machinery, and electrical equipment show that the country's infrastructure and industry are developing rapidly, offering chances for foreign investment and knowledge transfer. Building local manufacturing capability could also lessen vulnerabilities and promote long-term economic sustainability in two crucial areas: healthcare and food security, as indicated by the number of imports connected to pharmaceuticals and food.
Forecast Outlook: An Overview
It is forecast that Nicaragua's import outlook will expand moderately in 2025, in line with the country's expected 3.4% GDP expansion. Ongoing investments in the industrial and infrastructure sectors, as well as consistent remittance inflows that support private consumption, are anticipated to underpin this expansion. However, import growth may be hampered by global economic concerns, such as possible trade interruptions and shifting commodity prices.
Given the sustained need for consumer products, machinery, pharmaceuticals, and mineral fuels, the import composition is probably going to be stable. Attempts to increase domestic industrial capacity and diversify energy sources may eventually lessen reliance on specific imports. All things considered, Nicaragua's import industry is expected to increase steadily in 2025, although it is still vulnerable to outside economic forces and changes in international markets.
Conclusion
Between 2020 and 2024, Nicaragua's import profile shows a developing, consumption-based economy with close trade relations with both Asia and the Americas. The nation still depends significantly on foreign markets for essential infrastructural and consumer requirements, with energy, machinery, pharmaceuticals, and transportation equipment making up the majority of imports. Reducing economic risks and enhancing resilience would need sensible trade agreements, more local production, and strategic diversification. Sustainable economic development in Nicaragua as it enters 2025 will depend on addressing import dependency and preserving balanced growth.
If you are looking for detailed and up-to-date Nicaragua Import Export Global Data, You Can Contact Import Globals.
FAQs
Que: How much is Nicaragua's GDP expected to expand in 2024?
Ans: Nicaragua's GDP is expected to expand by 4.0% in 2024.
Que: In 2023, which nation was Nicaragua's biggest import partner?
Ans: In 2023, Nicaragua's biggest import partner was the United States, which accounted for 24% of all imports.
Que: In 2023, which product categories did Nicaragua import the most?
Ans: Mineral fuels, electrical machinery, automobiles, clothing, and machinery were the most popular import goods categories.
Que: What is the difference between 2020 and 2024 in Nicaragua's national debt as a percentage of GDP?
Ans: In 2020, Nicaragua's national debt was 65.4% of GDP; by 2024, it is expected to be 46.9%.
Que. Where to obtain detailed Nicaragua Import Data?
Ans. Visit www.importglobals.com or email info@importglobals.com for more information on up-to-date Nicaragua Import Data.
