
- Nov 08, 2025
Norway's Marine Trading Routes for Getting Products and Energy
It has a lot of resources, and its economy is one of the best in the world. As per Norway Import Trade Analysis by Import Globals, Norway is a significant part of world trade since it sells a lot of fish, oil, and gas.
But not many people know this: the country needs more and more specialized imports to maintain its energy infrastructure, shipbuilding expertise, and objectives for being green going. This is just another reason why it is so good at sending products to other countries.
Norway's energy and maritime import needs are changing quickly because of new technologies, a push for sustainability, and the desire to connect with the rest of the world. If you want to do business in one of Europe's most successful and forward-thinking countries, it's really important to understand how business works there.
Norway's Trade and Economy: A Look
Even though Norway only has roughly 5.5 million people living there, it boasts one of the highest GDPs per person in the world. This is because it has a lot of energy, a major shipping sector, and a complicated social safety net. As per Norway Import Data by Import Globals, The European Union (via the European Economic Area, EEA) and markets all over the world are very important to the country's economy.
People are still highly interested in what Norway sells, but the country is buying more and more, especially in sectors like green infrastructure, maritime technology, and energy equipment. As per Norway Export Data by Import Globals, this is helpful for businesses who sell products in their own country and businesses that sell things to individuals in other countries.
How Energy Imports Work
Everyone in the world understands that Norway's energy system is new and will last for a long time. Most of its electricity comes from hydropower and other renewable sources. The oil and gas business is also a large element of trade and the country's wealth, though.
The country needs to buy a lot of technical services, tools, and technology from other countries to keep things in this condition of equilibrium.
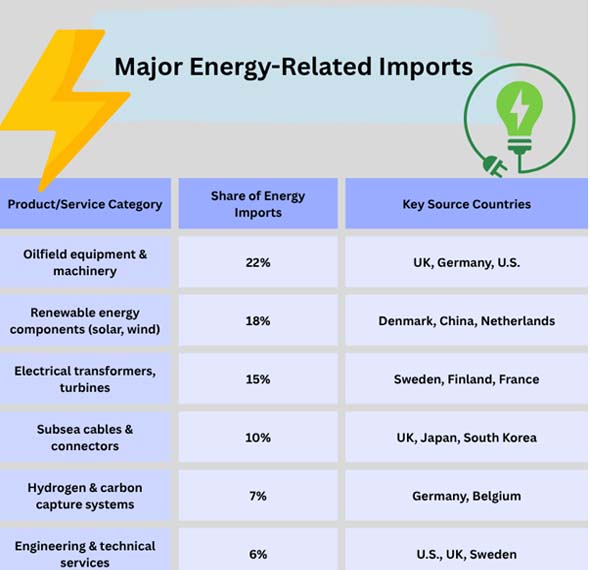
As per Norway Importer Data by Import Globals, Norway doesn't acquire power from other countries because it doesn't have enough resources. Instead, the country is committed to using new technologies and being good for the environment. To collect oil and gas from the water, you need special tools and machinery that are not from this planet. Renewable energy projects have to buy solar panels, wind turbines, and other technologies from other countries to make the system work better.
Bringing in goods and Going Green
As per Norway Import Trade Statistics by Import Globals, Norway wants to do better for the environment, thus it is utilizing less and less electricity from other countries. Energi21 is the government's long-term plan. It wants to go into carbon capture and storage (CCS), offshore wind, and hydrogen technology. As per Norway export data by Import Globals, to do this, it needs tools and information from other countries.
These are some key changes in imports that are making it easier to Switch to Cleaner Energy:
Ocean Wind Power: Norway gets a lot of different sorts of floating platform materials, turbines, and blades from Denmark, Germany, and the UK.
According to Import Globals' Norway Import Data, adding compressors, electrolyzers, and storage units will speed up the process of creating hydrogen fuel.
Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS): Norway is a leader in carbon capture initiatives like the Northern Lights Project because it uses technology from the Netherlands and Germany. People and businesses want smart meters, control systems, and heat pumps to help them save energy. This means that Norway buys technology to keep its green growth continuing and sells power. The maritime business needs imports and change to be strong.
As per Norway Import Shipment Data by Import Globals, Norway has one of the most advanced maritime industries in the world. It includes manufacturing ships, fishing, moving items, and working on oil rigs. Norway's marine infrastructure is in good shape, but they need to buy a lot of things to keep it that way.
Shipyards in Norway are constructing more and more specialized ships that are worth a lot of money. Some of them are research ships, support ships for work done at sea, and hybrid ferries. As per Norway Import Export Trade Analysis by Import Globals, they need complicated software, navigation systems, and propulsion systems that they can't get in their own country.
It's also necessary to bring in new technologies from other nations because of the transformation to green shipping, which uses hydrogen, ammonia, and electricity to move things. Norway needs to work with suppliers in Europe and Asia to modernize its shipping industry.
Roads and Buildings for Work
Oslo, Bergen, Stavanger, and Trondheim are among of Norway's most important ports. They make it easier for goods to enter and leave the country. As per Norway Export Import Global Trade Data by Import Globals, it is one of the most reliable trading centers in Europe right now because of its great infrastructure and up-to-date customs processes.
Important Parts of Norway's Trade Routes
Joining the EEA: Norway is a member of the EEA, therefore it can trade most goods with the EU without having to pay tariffs.
Maritime Corridors: Ports that are part of European transportation networks make it easier for products to get where they need to go. Over time, more trade routes in the Arctic will help bring in shipping and energy.
Digital Trade Systems: As per Norway Import Data by Import Globals, with e-commerce and online customs forms, it's simple to transfer goods to other nations. This link helps Norway keep its supply chains going even when things go wrong in other parts of the world.
Opportunities for Exporters Around the World Norway keeps investing in green energy and maritime technology, which allows exporters and inventors from all over the world a lot of opportunity to do business. Businesses need to sell more and more products that can be used again, such solar panels, offshore wind turbines, and hydrogen technologies.
Marine Engineering and Ship Parts: There is a big need for trustworthy suppliers of engines, navigation systems, and hybrid propulsion systems. The maritime automation and energy analytics industries are growing the quickest right now.
Using clean manufacturing practices, CCS technology, and recycling systems are all great ways to lower carbon emissions and make things last longer. If companies from other nations fulfill Norway's criteria for engineering and the environment, they can receive good, stable contracts.

Issues and Shifts in the Market
The market in Norway is great for business, however it could be hard for new enterprises to get started. Following strict standards and getting a Certificate: There are strict standards that must be followed to safeguard the environment and make sure the quality is good.
Currency Volatility: The value of the Norwegian Krone can shift, which can influence how much money you make on a deal.
High Cost Base: Running a business in Norway is one of the most expensive areas in Europe.
Competitive Tendering: Most big contracts are open for bids, however the process is exceedingly hard.
Norway is still a safe area to do business since the government is stable, the laws are clear, and the business climate is straightforward to understand.
Last Words
Norway's trade profile shows a paradoxical kind of wealth: it sells a lot of energy yet has to buy more and more advanced technologies to be competitive in the world. Exporters from all over the world who care about the environment and new ideas have a lot of chances because the country's energy and shipping industries are changing. Norway seeks to make its economy more environmentally friendly, cleaner, and efficient. But it will still need to get items from other countries to develop the next generation of green infrastructure and maritime excellence. Import Globals is a leading data provider of Norway import export trade data.
FAQs
Que. What does Norway acquire from other countries that is the most important?
Ans. Norway often buys parts for ships, computers, industrial machinery, and technology that makes energy.
Que. Why does Norway sell energy yet buy equipment to make energy?
Ans. It gets innovative technologies from other countries to use in oilfield work, projects that use renewable energy, and converting to green energy.
Que. Where does Norway acquire most of its stuff?
Ans. Germany, the UK, Sweden, China, and the Netherlands provide most of the energy and nautical items to the US.
Que. How likely is it that exporters from other countries will do well?
Ans. Renewable energy systems, marine automation, hydrogen infrastructure, and smart ship technologies all have a lot of attractive job openings.
Que. Where can you obtain detailed Norway Import Export Global Data?
Ans. Visit www.importglobals.com or email info@importglobals.com for more information on up-to-date data.
