
- Sep 25, 2025
Russian Oil Exports in 2025: Navigating Sanctions and Sustaining Trade
In 2025, based on Russia Import Data by Import Globals, due to Western sanctions, price limitations, and compliance procedures increasing pressure, Russia has proven amazing agility by shifting barrels to Asia, employing clever pricing, and managing a maze of logistics obstacles. But under the surface, Russia's budgetary roots are being tested, an undercurrent that requires careful and critical examination.
Asia Takes the Helm: India and China Lead
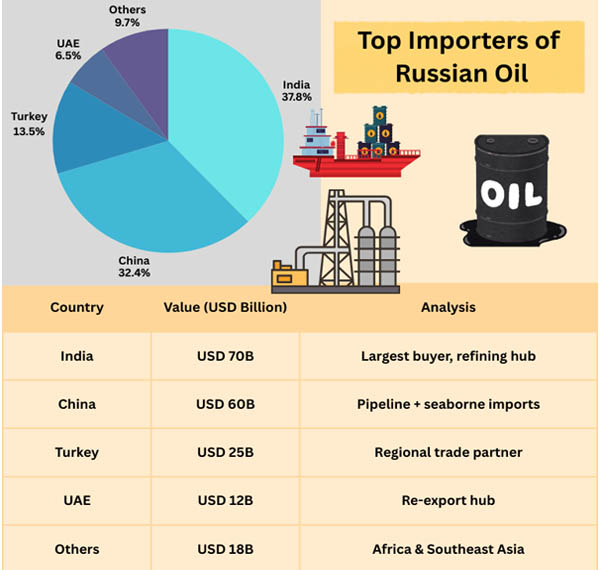
Russia's worldwide reach has evolved, but its dependency on Asia has only grown. According to China Export Data by Import Globals, China will account for around 45%-50% of total petroleum exports in 2025, anchoring demand with both long-term contracts and opportunistic purchases. Despite foreign diplomatic pressure, India remains a formidable alternative outlet at 35%-40% due to improved arbitrage and term flexibility. While European demand has fallen to fewer than 10% of the export mix, Turkey, Southeast Asia, and Latin America continue to give rare product-differentiated signals.
Transition from Europe to Asia
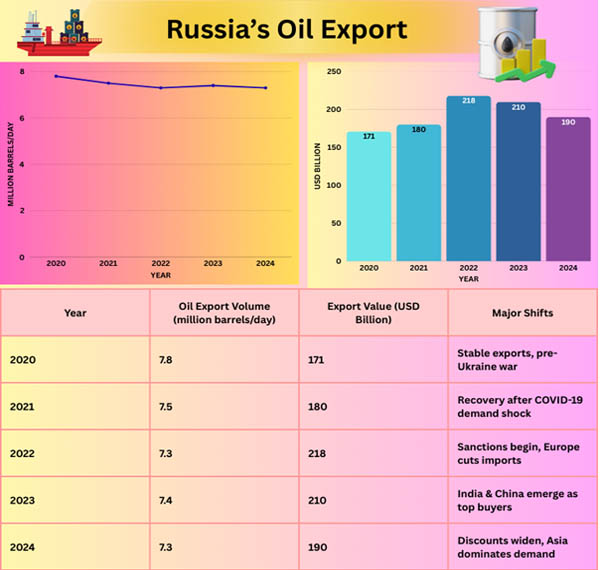
Before the Ukraine war, the European Union was Russia's largest oil consumer, purchasing roughly half of Russian petroleum. However, as per Ukraine Import Export Trade Data by Import Globals, with the EU ban in December 2022, trade patterns changed radically. Currently, Asia accounts for more than 75% of Russia's oil exports, headed by
- India is the top importer, purchasing cheap Urals oil for processing and re-export.
- China - Long-term strategic partner for pipeline and seaborne imports.
- Turkey is an important regional customer, balancing Western ties with Russian energy demands.
Sanctions and Price Caps: Adapting to Pressure
The G7's oil price limitation limits service assistance (insurance, transportation) for Russian crude that exceeds $60 per barrel. Russia Import Custom Data by Import Globals indicates that insurance and maritime corporations based in G7 countries have generally withdrawn from sanctioned operations. To comply with increased inspection, shadow fleet engagement decreased significantly, from 17% in January to 40-45% by mid-2025.
Results & Market Responses
Rising freight costs to Asia lower netbacks, particularly for long-haul exports. Discount margins (originally 20-30%) have shrunk as markets return to normalcy, but they will tighten more if supply is curtailed or enforcement becomes more stringent.
Russia Import Trade Analysis by Import Globals suggests that product exports suffer from increased paperwork scrutiny, with seaborne refined shipments down 6% month on month in July, while crude remained stable. To preserve competitiveness under sanctions, Russia sells petroleum at a discount of USD 10-15 per barrel to Brent crude. This strategy contains:
- Increased demand in India and China.
- Reduced overall export revenue while ensuring market stability.
- Created a "shadow fleet" of tankers, avoiding Western insurers.
Revenue Reality: Flow ≠ Profit
While barrels roll out, the money does not always follow in full. In June 2025, oil and gas revenues decreased by around 34% compared to the previous year, while overall income decreased by about 20% from January to June. Lower per-barrel margins, despite relatively stable pricing, are compounded by a higher ruble and operational problems, putting fiscal health under strain. Russia's export numbers remain resilient. However, as per Russia Export Data by Import Globals, declining per-barrel earnings represent an increasing challenge to fiscal stability and domestic spending objectives.
Shadow Fleet and Alternative Trade Routes
Russia transports petroleum using a fleet of outdated oil ships that lack Western insurance and tracking. This "shadow fleet" accounts for 70% of Russia's seaborne oil traffic. Based on Russia Import Data, new routes through the Suez Canal, Arctic maritime channels, and Asian ports have transformed trade logistics.
Looking ahead: Strategic Minefields and Growth Paths
Five developments may transform Russia's oil export landscape from 2025 to 2030:
- Sustained Pull from Asia - China's strategic inventory buildup and India's improving economies may continue to support Russian exports.
- Sanctions Tightening - If insurance and shipping clusters impose stricter compliance requirements, transaction costs would rise, putting margin viability to the test.
- Global Oil Price Dynamics – As per Russia Import Trade Statistics, big Brent surge broadens price caps' impact; discounts may be required to keep barrels flowing.
- Refined Product Strategy - For operational flexibility, Russia may choose crude shipments to more complex and sanctioned refined cargoes.
- Fiscal Rebalancing - Prolonged income deficits may force Russia to reallocate spending or seek new market-access agreements to maintain trade volumes.
Conclusion
Russia's oil exports in 2025 tell a story of perseverance combined with weakness. The country maintains consistent quantities by shifting to Asia, implementing tactical pricing, and managing new transportation dynamics. However, extracting true value despite declining discounts, rising prices, and fiscal hardship is becoming a more difficult balancing act. China Import Data by Import Globals suggests that trade watchers and industry experts should keep an eye on buyer behavior in India and China, enforcement developments in shipping corridors, and energy price trends for early signs of disruption or recalibration. Import Globals is a leading data provider of Russia import export trade data. Subscribe to Import Globals to get more global trade details!
FAQs
Que. Is Russia still a major oil exporter in 2025?
Ans. Yes, as per Russia Export Import Global Trade Data, despite sanctions and trade friction, Russia remains one of the top crude exporters globally, with export volumes nearly matching 2024 levels.
Que. Who are the main buyers of Russian oil this year?
Ans. China (45–50%) and India (35–40%) dominate the buyer mix, with minor flows still reaching Europe, Türkiye, Brazil, and parts of Southeast Asia.
Que. How have sanctions affected Russia’s oil revenues?
Ans. Revenue per barrel has been squeezed by narrower margins, rising transportation costs, and a stronger ruble, leading to a 34% drop in June 2025 oil and gas income versus a year earlier.
Que. What could change Russia’s oil trade trajectory in the near term?
Ans. Key variables include: stricter enforcement of shipping/insurance sanctions, shifts in India–China demand, global oil price dynamics, and Moscow’s budget adaptation strategies.
Que. Where can you obtain a detailed Russia Import Export Trade Analysis?
Ans. Visit www.importglobals.com or email info@importglobals.com for more information on up-to-date data.
