
- Sep 27, 2025
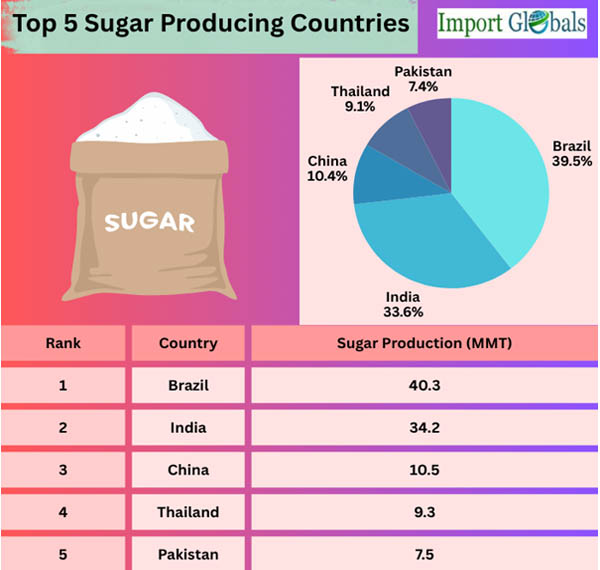
Top 5 Sugar Producing Countries in the World
With commerce and production worth billions of dollars across continents, the global sugar sector is enormous.
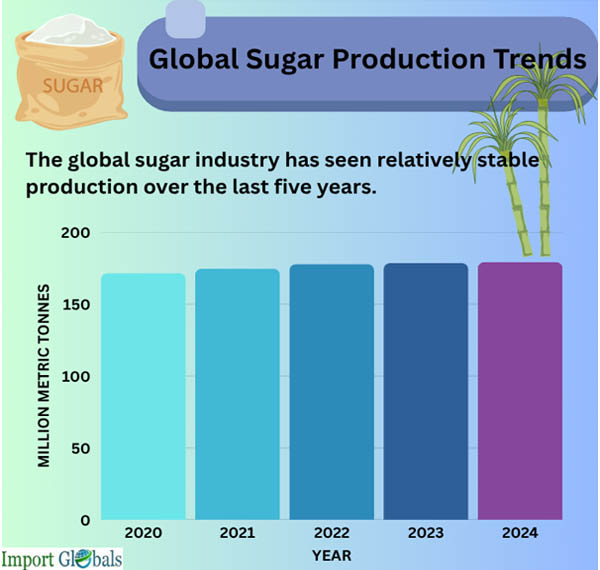
Based on Sugar Import Data by Import Globals, around 179 million metric tons of sugar are produced worldwide as of 2024, with tropical and subtropical nations producing the majority of this total. The top five sugar-producing countries are examined, production patterns are examined, and statistical insights are provided to help visualize the global sugar business.
Brazil: The World's Leading Sugar Producer
Brazil continues to lead the world in sugar production, accounting for more than 22% of total production in 2024. São Paulo state, where extensive sugarcane farms and perfect growth conditions are created by good weather, produces the majority of Brazil's sugar. Based on Brazil Export Data by Import Globals, about 45% of Brazil's sugarcane is processed for bioethanol, demonstrating the close integration of the country's sugar economy with the production of ethanol fuel.
Brazil is the biggest exporter of sugar, reaching important markets like China, Indonesia, and the EU because of its extensive infrastructure and high demand worldwide.
India: With enormous domestic demand, it comes in second.
In 2024, as per India Import Export Trade Data by Import Globals, 34.2 million metric tons of sugar will be produced in India, the world's second-largest producer. India consumes most of its sugar locally, in contrast to Brazil. Production is dominated by states like Karnataka, Maharashtra, and Uttar Pradesh.
Additionally, the sugar sector in India directly and indirectly supports more than 50 million farmers. Production levels are frequently impacted by government price limits and subsidies. India's exports have also grown recently, especially to the Middle East and Indonesia.
China: Increasing Production at Home
With an estimated 10.5 MMT of sugar production in 2024, as per China Import Data by Import Globals, China comes in third. Despite not being a significant exporter, China's primary sugar-producing regions are Guangxi and Yunnan, both of which offer temperatures that are ideal for growing sugarcane and sugar beets.
Although China's per capita sugar consumption is lower than that of the West due to growing health consciousness, the nation is still one of the world's largest users, which maintains its high import requirements despite domestic production.
Thailand: Expert in Sugar Export
Thailand is one of the world's biggest exporters, second only to Brazil, with an estimated 9.3 MMT of sugar produced in 2024. As per Thailand Export Data by Import Globals, the Thai government has made significant investments in mechanical milling and growing methods for sugarcane. The nation sells sugar to Indonesia, Japan, and some regions of Africa, and the sector is well-supported by infrastructure.
Thailand maintains its competitiveness because of its efficiency and solid trade relations, even in the face of sporadic droughts.
Pakistan: Remaining Firm Despite Obstacles
Despite energy problems and water scarcity, as per Pakistan Import Data by Import Globals, Pakistan continues to rank in the top five with 7.5 MMT in 2024. The provinces of Sindh and Punjab cultivate the majority of sugarcane. Despite price disputes, export restrictions, and regulatory changes, Pakistan's sugar sector is still a major employer and GDP contributor.
Depending on surplus supply, Pakistan also sells sugar to Afghanistan, Sri Lanka, and East African countries.
Trends in Sugar Consumption and Upcoming Demand
Global sugar consumption is still rising even if production is leveling down, especially in developing nations like Nigeria, Indonesia, and India. On the other hand, health laws and sugar levies are causing a decline in certain Western nations. Based on Indonesia Import Trade Statistics, Global sugar consumption is expected to reach 176 million metric tons by 2024.
The following factors are expected to push the worldwide demand to reach 185–190 MMT by 2030:
- Demand from the processed food and beverage sector has increased.
- Higher incomes and urbanization in developing countries
- The ongoing manufacturing of ethanol from sugarcane
Sugar Prices' Effect on the World Economy
The energy market, industrial expenses, and food inflation are all greatly impacted by sugar prices. Based on Brazil Import Data by Import Globals, due in large part to the climate in Brazil and India, as well as the price of crude oil globally (which affects the demand for ethanol), sugar prices in 2023–2024 ranged between 18 and 23 U.S. cents a pound.
Important factors influencing prices include
- Weather patterns (droughts or floods in countries that produce)
- Tariffs and government subsidies
- Because sugarcane is linked to ethanol, oil prices
- Changes in currency, particularly the Indian Rupee and Brazilian Real
- Price increases for sugar often occur:
- Increase the price of processed foods, soft drinks, and confections.
- Encourage nations to combine more ethanol since sugarcane is becoming a more valued fuel.
- Put pressure on importing countries' economies to raise food prices.
Sustainability and Environmental Difficulties
Based on the Sugar Import Export Trade Analysis, there are environmental costs associated with sugar production:
- Deforestation: Because of growing plantations, especially in Brazil and Thailand.
- Water Use: The cultivation of sugarcane in India puts a burden on local water supplies since it requires a lot of water.
- Carbon Footprint: Emissions of CO2 are caused by the usage of fertilizer and milling operations.
Today, nations are moving in the direction of:
- Water-saving drip irrigation systems
- Mill waste-to-energy systems
- Government policies to promote green practices (especially in Brazil)
Innovations in Sugarcane Farming Technology
Based on Sugar Export Import Global Trade Data, several nations that produce sugar are implementing agri-tech solutions to fulfill the growing demand and lessen their impact on the environment:
- Water Consumption: It can be cut by up to 50% with drip irrigation systems (India, Brazil).
- Drone and Satellite Monitoring: Assist in tracking insect infestations and crop health in Thailand and Brazil.
- AI Prediction Tools: India uses AI-based yield prediction tools to encourage more intelligent harvesting.
- Smart Mills: Thailand and Brazil have adopted energy-efficient mills that produce bagasse-based bioenergy (power from cane waste).
- Precision Agriculture: Farmers are applying fertilizer only where it is required by utilizing sensors and apps.
These advancements are not just improving yields but are also helping make sugar production more sustainable and cost-efficient.
Concluding Remark: Sugar Production's Future
Sugar will continue to be an essential commodity for both direct consumption and industrial applications as the world's population grows. While nations like China and Thailand prioritize sustainability and efficiency, nations like Brazil and India will continue to rule. The sugar industry will be shaped for many years to come by trade policy, innovation, and climate change. Import Globals is a leading data provider of Vietnam Import Export Trade Data. Subscribe to Import Globals to get more global trade details!
FAQs
Que. Which country produces the most sugar in 2024?
Ans. Brazil, with 40.3 million metric tons, holds the top spot.
Que. Is India a major sugar exporter?
Ans. Yes, though most sugar is consumed domestically, India exports surplus sugar to Asia and the Middle East.
Que. Why is sugar production important?
Ans. It supports millions of livelihoods, contributes to GDP, and serves multiple industries, including food and fuel.
Que. What are the top challenges in sugar production?
Ans. Water scarcity, climate change, price fluctuations, and environmental impacts are key concerns.
Que. Where can you obtain detailed Sugar Import Export Global Data?
Ans. Visit www.importglobals.com or email info@importglobals.com for more information on up-to-date data.
