
- Aug 22, 2025
Zimbabwe Export Performance and Economic Outlook
Along with fertile territory that enables the production of important agricultural exports like cotton and tobacco, the nation is blessed with enormous mineral deposits, including gold, platinum, and diamonds.
As per Zimbabwe Import Data by Import Data, Zimbabwe's export industry has shown resilience in the face of economic challenges like inflation, currency volatility, and structural inefficiencies, and it continues to be a vital source of foreign cash revenues and job creation.
Zimbabwe has worked to boost value addition through domestic raw material processing and diversify its export base in recent years. As per Zimbabwe Export Data by Import Globals, the country's export outlook is cautiously hopeful due to developing trade partnerships spanning Africa, Asia, and Europe, as well as emerging potential in the lithium sector. This blog examines Zimbabwe's export performance between 2020 and 2024, focusing on export data, main trade destinations, economic indicators, important product categories with HS codes, and emerging trends influencing the country's trade path.
Zimbabwe's Key Economic Indicators
Over the last five years, Zimbabwe's economy has gone through periods of both improvement and instability. The nation recovered with modest growth in 2021 and 2022, propelled by increased agricultural output and mineral exports, following a severe recession in 2020 brought on by COVID-19 and recurrent droughts. However, severe unemployment, currency depreciation, and ongoing hyperinflation still impede long-term improvement. As per Zimbabwe Import Export Trade Data by IMPORT GLOBALS, rapid devaluation of the Zimbabwean dollar has made it challenging to preserve investor confidence and price stability, and inflation rates have continued to rank among the highest in the world.
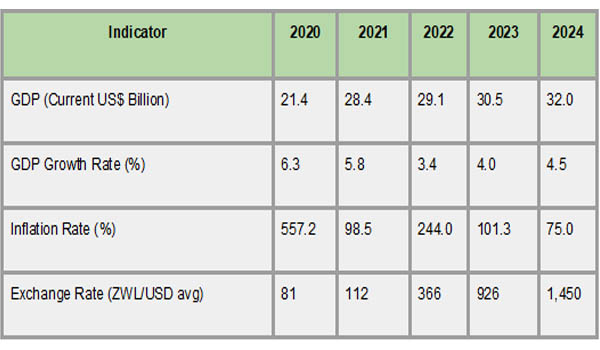
The macroeconomic situation has been steadily stabilized despite these obstacles. Recent years have seen GDP growth of roughly 4% to 5%, helped by advantageous commodity prices and well-timed mining and agricultural developments. As per Zimbabwe Import Custom Data by Import Globals, the government's efforts to boost productivity and export competitiveness, as well as its fiscal and monetary reforms, provide cautious hope for future expansion. Highlighting both advancements and persistent vulnerabilities, the following table provides a summary of the nation's major economic indicators from 2020 to 2024.
Major Export Product Categories of Zimbabwe
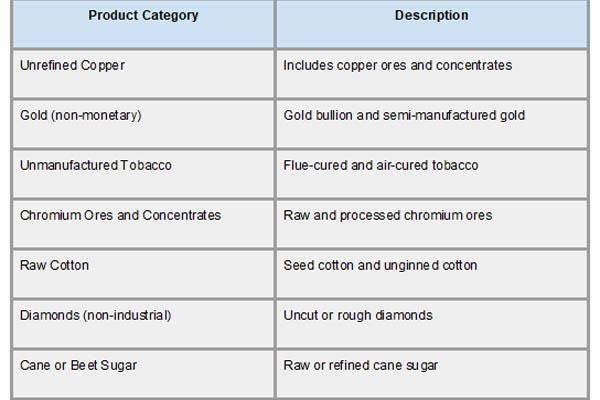
The mainstay of Zimbabwe's trade economy, agricultural and mineral commodities make up the majority of its export portfolio. With a substantial portion of overall revenue, gold continues to be the most important export. Tobacco, particularly flue-cured Virginia tobacco, which is highly regarded for its quality worldwide, comes in second. As per Zimbabwe Import Trade Analysis by Import Globals, diamonds, ferrochrome, and platinum group metals (PGMs) are further essential mineral exports. Since these resources are extracted in their raw or semi-processed state, they are extremely susceptible to changes in the price of commodities globally.
Aside from minerals, agricultural exports like sugar and raw cotton also play a significant role. However, a large portion of these commodities are exported in raw or unmanufactured form due to a lack of sophisticated local processing facilities. This highlights a crucial chance for Zimbabwe to transition to value addition, which may greatly increase export earnings and generate job opportunities. The export structure of the nation, as described by worldwide HS (Harmonized System) codes, emphasizes the need for long-term industrialization and diversification while also reflecting its significant reliance on primary exports.
Zimbabwe’s Export Performance
With total exports rising from roughly US$4.39 billion in 2020 to US$7.43 billion in 2024, Zimbabwe's export industry showed a steady increase trajectory between 2020 and 2024. Strong results in the mining and agricultural industries, particularly in the areas of gold and tobacco, were the main drivers of this rise. As per Zimbabwe Export Data by Import Globals, together, tobacco and semi-manufactured gold exports accounted for almost half of the country's export revenue in 2024, with tobacco exports totaling US$1.3 billion and semi-manufactured gold exports reaching US$2.54 billion. Nickel ores and concentrates (US$472 million) and nickel mattes (US$989 million) were other major contributors.
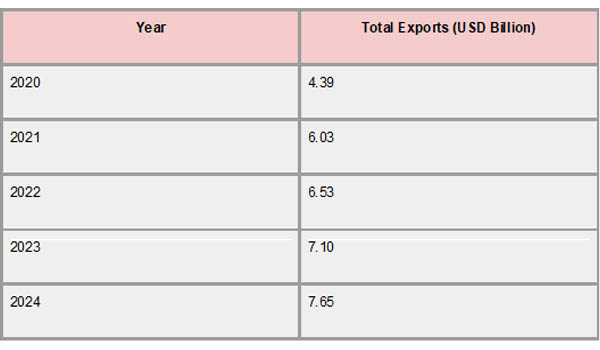
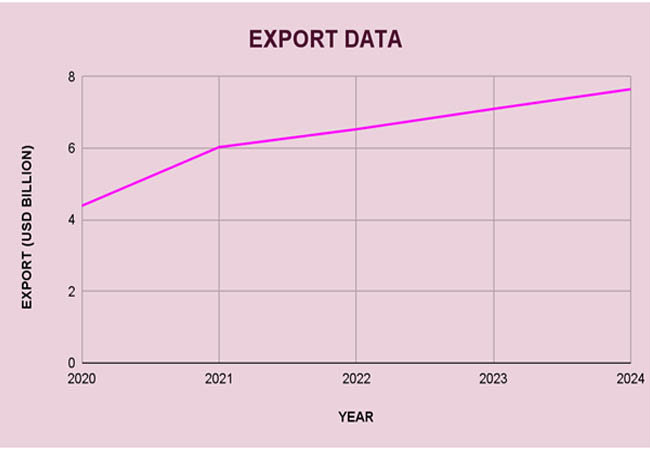
Despite these improvements, imports grew faster than exports, resulting in a US$9.53 billion trade deficit in 2024, which increased to US$2.1 billion. Value-added items make up just 5.9% of total exports, down from 6.2% in 2023, indicating that the export basket is still largely dependent on raw commodities. Nonetheless, as per Zimbabwe Import Data by Import Globals, there were encouraging gains in value-added exports, which increased by 2.3% to US$290.9 million, and horticulture, which increased by 12.4% to US$59.8 million. These patterns show that to improve economic resilience and lessen susceptibility to changes in the price of commodities globally, Zimbabwe must diversify its export base and make investments in domestic processing.
Major Export Destinations
Three major trading partners, China, South Africa, and the United Arab Emirates (UAE), dominated Zimbabwe's export market in 2024. At over 36.7% of Zimbabwe's total exports, which are valued at about US$2.7 billion, the UAE emerged as the top export destination. As per Zimbabwe Import Trade Statistics by Import Globals, this notable expansion demonstrates how Zimbabwe and the UAE's economic relations are growing, especially in the trading of agricultural and mineral goods. South Africa, which received roughly 28.9% of Zimbabwe's exports, or US$2.15 billion, continued to be an important regional partner. China's 18.3% export contribution, or US$1.36 billion, was fueled by its demand for Zimbabwean resources, particularly nickel and chrome.
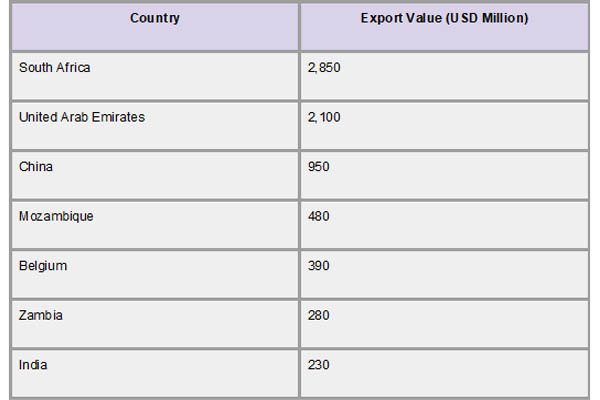
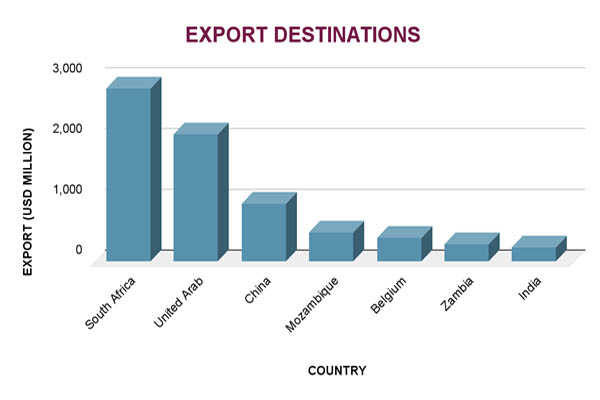
Zimbabwe has been aggressively expanding its export destinations beyond these core markets. As per Zimbabwe Import Shipment Data by Import Globals, exports to Zambia and Mozambique increased significantly, fueled by infrastructure improvements and regional trade initiatives. Furthermore, emerging markets like Vietnam, Hong Kong, and Indonesia have seen encouraging development, which is indicative of Zimbabwe's attempts to increase its global trade presence. Notwithstanding these developments, the concentration of exports to a small number of nations emphasizes the necessity of additional diversification to reduce the risks associated with market dependence.
Strategic Implications and Forecast Trend
Strategic measures focused on diversification, value addition, and market expansion are driving a revolutionary phase in Zimbabwe's export industry. Participation in events like the Zimbabwe International Trade Fair (ZITF), which promotes investment discussions and displays export prospects, demonstrates the country's dedication to improving trade competitiveness. As per Zimbabwe Import Export Trade Analysis by Import Globals, with a noteworthy 15% increase in shipments to the UK in 2023, efforts to access markets like the UK without tariffs have paid off. Furthermore, the emphasis on investments in renewable energy and sustainable agriculture is in line with global trends, putting Zimbabwe in a position to satisfy the changing needs of global markets.
Zimbabwe has a cautiously optimistic export forecast for 2025. A resurgence in agricultural production and a rise in mining activity, especially in lithium, are expected to support economic growth as it recovers to about 6%. Nonetheless, as per Zimbabwe Export Import Global Trade Data by Import Globals, there are still issues, such as inadequate infrastructure, inconsistent policies, and outside variables like fluctuations in commodity prices. To maintain export growth, the government must prioritize value addition, particularly in the mining industry, and work to enhance the business climate. Long-term economic stability and the realization of Zimbabwe's full export potential will depend on sustained infrastructure investment and supportive policies.
Conclusion
Due in significant part to its abundant mineral resources and robust agricultural foundation, Zimbabwe's export industry has demonstrated exceptional resilience and development between 2020 and 2024. As per Zimbabwe Import Export Global Data by Import Globals, the nation is progressively investigating new markets and industries like lithium and horticulture, even as traditional exports like gold, tobacco, and platinum continue to dominate the market. However, Zimbabwe needs to diversify its export base, invest in value addition, and address structural issues like infrastructure and policy coherence if it hopes to achieve sustainable growth and lessen its susceptibility to international shocks. The country has a great chance to become a more competitive participant in international trade with sustained reforms and strategic emphasis.
If you are looking for detailed and up-to-date Zimbabwe Export Data, You Can Contact Import Globals.
FAQs
Que. What are Zimbabwe’s top 3 export products?
Ans. Gold, tobacco, and platinum are the top export products by value.
Que. Which country is Zimbabwe’s largest export partner?
Ans. South Africa is the leading export destination for Zimbabwean goods.
Que. What role does gold play in Zimbabwe’s exports?
Ans. Gold is the top export, contributing nearly 30–35% of total export earnings.
Que. Is Zimbabwe part of any trade agreements?
Ans. Yes, including the SADC Free Trade Area, COMESA, and the AfCFTA.
Que. What is Zimbabwe’s export outlook for 2025 and beyond?
Ans. Exports are expected to grow steadily, driven by mineral beneficiation, lithium demand, and regional trade opportunities.
Que. Where to obtain detailed Zimbabwe Import Data?
Ans. Visit www.importglobals.com or email info@importglobals.com for more information on up-to-date Zimbabwe Import Data.
