
- Sep 15, 2025
German Industrial Production: Signs of Revival Amid Persistent Headwinds
However, the nation's industrial foundation has been under tremendous strain over the last two years. As per Europe import data by Import Globals, output was weakened by a combination of high energy prices, changing international trade regulations, supply chain interruptions, and low domestic demand.
However, a startling occurrence in May 2025 offered cautious hope: a robust uptick in German industrial production suggested that recovery could finally be underway. The specifics of the recovery, industry drivers, underlying concerns, and wider ramifications for Germany's economy are all examined in this blog.
Key Points
In May, German industrial production increased by 1.2% month-over-month after shrinking a steep 1.6% in April. This gave the market its first significant upswing in months and surpassed market predictions of stagnation. Germany Export Data by Import Globals reflects that output increased 1.0% year over year, reversing a 2.1% decline in April and representing the largest annual growth since early 2023.
Given that Germany's industrial sector had been steadily declining since late 2022 and that output levels were still around 6% below their pre-slump peak, the recovery is especially noteworthy. The May bounce shows that there are signs of recovery, even though it does not completely erase those losses.
Sectoral Factors Contributing to the Growth
Automobile Manufacturing
USA Import Export Trade Data by Import Globals indicates that Germany's renowned automotive industry was the best-performing, with a 4.9% rise in output in May. U.S. importers front-loading purchases in anticipation of possible tariff rises contributed to this spike. Germany is still the top exporter of automobiles in Europe, and the industry's tenacity remains a cornerstone of the national economy.
Pharmaceutical Production
With a 10% increase, the pharmaceutical sector performed even better. Exports were increased by the worldwide need for medical supplies and tariff exemptions on specific pharmaceutical items. As per Germany Import Data by Import Globals, Germany's well-established pharmaceutical industry is turning out to be a significant growth engine, especially in the fields of biotechnology and specialty drugs.
Production of Energy
Due to increasing activity in domestic electricity and power generation, energy production grew by 10.8%. In addition to boosting industrial activity, this surge helped strengthen energy-intensive sectors like metals and chemicals.
Energy-Intensive Industries and Construction
On the other hand, building production decreased 3.9%, extending a long-term decline linked to high borrowing costs and weak demand for real estate. Europe Import Trade Analysis by Import Globals states that Energy-intensive sectors like chemicals and basic metals also saw a 1.8% decline, underscoring the ongoing pressure from high energy prices and structural issues.
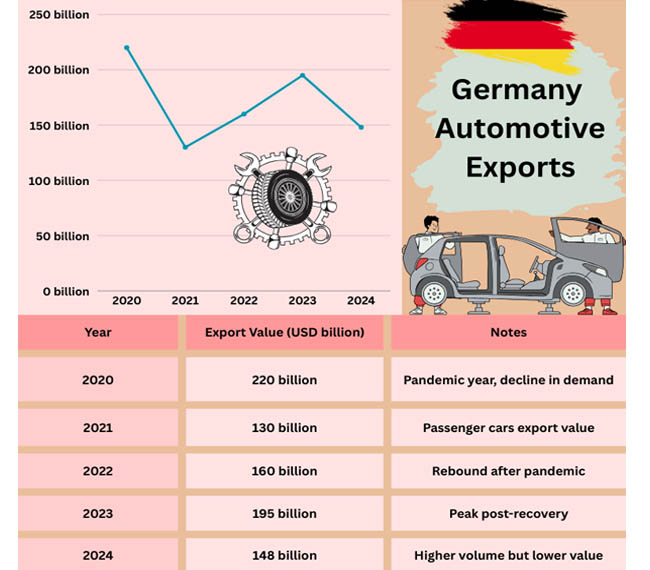
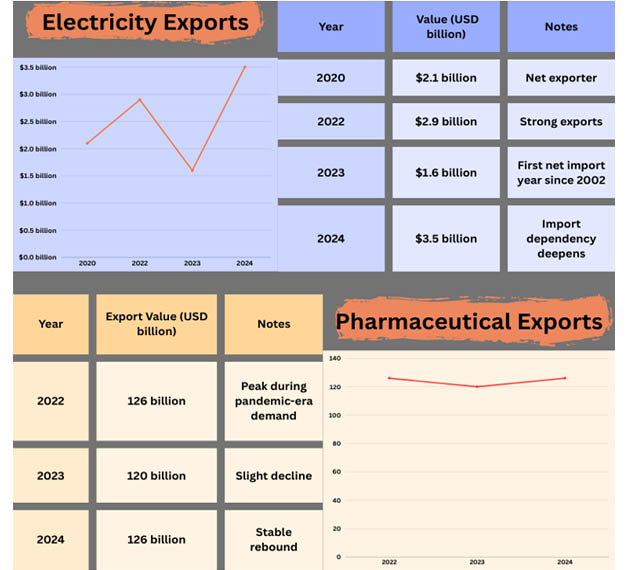
Overarching Patterns and Three-Month Results
In comparison to the preceding three months, industrial production increased 1.4% during the March–May three-month period. This volatility smoothing indicates that the comeback was a part of a longer-term trend rather than just a one-month fluke.
Despite the stabilization of output, order books reveal a different picture. Germany Export Data by Import Globals reveals that May saw a 1.4% decline in manufacturing orders, mostly as a result of decreased demand from partners in the eurozone. Metal items, capital goods, and electronics were especially heavily impacted. This discrepancy between orders and output emphasizes how fragile the recovery is.
Fundamental Factors and Resilience
Front-Loading and Tariff Pressures
Front-loading exports was a major factor in May's impressive result. Orders from Germany increased as U.S. consumers anticipated 25% levies on European cars and other items. Although this gave a temporary lift, once tariffs are completely applied, it raises concerns about sustainability.
Assistance from the Government
In an effort to boost industrial competitiveness, Berlin has proposed a set of tax breaks and investment incentives. As per Europe Import Data by Import Globals, it is anticipated that further infrastructure expenditure, such as public works and defense upgrading, will increase demand in key industries. These actions, together with the European Central Bank's lowered interest rates, may assist in maintaining momentum.
Strength of Exports against Weakness at Home
Currently, exports are driving Germany's recovery. However, domestic demand is still low, particularly for consumer durables and construction. Stronger household spending and demand in the eurozone will be necessary for industrial production to continue growing.
Obstacles & Risks to Come
Cost and Energy Pressures
Energy costs are still greater than they were before the crisis, despite a decline from their 2022 highs. Overall performance is hampered by the continued lag of energy-intensive industries. Germany is still pushing for renewable energy, but it will take time and sustained investment until the full advantages are realized.
Increased Trade and Euro Competitiveness
Europe Import Trade Statistics by Import Globals reflects that by raising the cost of German goods on international markets, a stronger euro creates further difficulties. If the currency keeps rising in value relative to the dollar and other major currencies, export-led growth may be put under pressure.
Issues with the Supply Chain and Transportation
Major rivers like the Rhine now have lower water levels due to the exceptionally dry summer, which has disrupted inland transportation and increased logistical expenses. These constraints are making cost pressures worse since river transportation is essential for industrial commodities and raw materials.
Issues with Structure
Germany Export Import Global Trade Data indicates that Germany's industrial production is still well behind its pre-2022 peak, even with the May recovery. An aging workforce, sluggish adaptation in energy-intensive industries, and dependence on outside demand are just a few of the structural problems that still plague the industry.
Prospects: A Delicate Comeback
The manufacturing sector in Germany is at a turning point. On the one hand, the May recovery shows that important sectors like energy, pharmaceuticals, and autos are resilient. However, without more significant structural changes, the recovery may not last long due to concerns of trade tensions, high prices, and weak domestic demand.
Germany's industrial sector may progressively regain lost ground if government initiatives are successful in boosting investment and removing obstacles, as well as if export demand is high. However, given the uncertainty surrounding global trade and energy concerns, firms and governments need to be ready for volatility. Import Globals is a leading data provider of Germany Import Export Trade Data. Subscribe to Import Globals to get more global trade details!
FAQs
Que. How much did German industrial production grow in May 2025?
Ans. It increased by 1.2% month-on-month and 1.0% year-on-year, reversing April’s sharp contraction.
Que. Which sectors contributed most to the rebound?
Ans. As per Germany Import Export Trade Analysis, Automobiles (+4.9%), pharmaceuticals (+10%), and energy (+10.8%) led the growth, offsetting declines in construction and energy-intensive industries.
Que. What are the main risks for Germany’s industrial sector?
Ans. Key risks include weak domestic demand, potential tariff impacts, high energy costs, a stronger euro, and structural challenges in heavy industries.
Que. Is the recovery sustainable?
Ans. The May rebound is encouraging but partly driven by temporary factors like export front-loading. Long-term sustainability depends on structural reforms, domestic demand revival, and global trade stability.
Que. Where can you obtain detailed Germany Import Export Global Data?
Ans. Visit www.importglobals.com or email info@importglobals.com for more information on up-to-date data.
