
- Dec 23, 2025
Important Imports for the Swedish Economy
Sweden has one of the most trade-integrated economies in Europe. It exports high-tech goods and services and imports the fuels, parts, and other specialized inputs that keep its factories operating and its homes stocked.
As per Sweden Import Data by Import Globals, This openness is a plus because it lets Swedish businesses connect to global value chains. However, it also makes it evident that Sweden is dependent on imports, which is important for inflation, industrial competitiveness, and supply security.
As per Sweden Export Data by Import Globals, Sweden bought goods of about SEK 1,997 billion in 2024, which was a little drop from 2023 (both in value and volume). That big number hides an important fact:
Swedish imports aren't only about what people buy; they're also significantly influenced by what businesses need (machines, electronics, automobiles, chemicals, fuels, and intermediate inputs). To properly appreciate Sweden's dependence on imports, you need to know which foreign inputs are the toughest to quickly replace without stopping production or boosting costs. One line on Sweden's dependence on imports: Energy and industrial inputs
Sweden's import Profile has stayed the Same over the Years
As per Sweden Import Export Trade Data by Import Globals, Sweden doesn't produce any crude oil, yet it still needs oil products for transportation and industry.
Sweden is a leader in innovative manufacturing and transportation, and it imports a lot of valuable things like machinery, electrical equipment, and cars. Chemicals and medicines are very important for supply chains in healthcare and industry.
As per Sweden Import Custom Data by Import Globals, electronics and telecom gear are the backbone of everything from home appliances to automated factories. Food inputs and agricultural goods are more important amid price shocks and supply problems, even if they aren't necessarily the most valuable things.
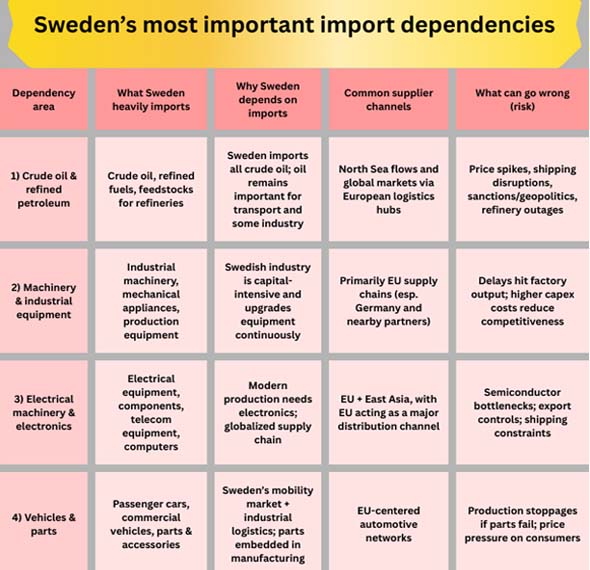
The most important question for firms and politicians is not "Does Sweden import a lot?" "Which imports would be the most shocking if they were stopped?"
1) Energy: Crude Oil is the Most obvious Structural Dependency
Energy, especially crude oil, is the most important structural dependency. As per Sweden Import Trade Analysis by Import Globals, Sweden doesn't make crude oil itself; instead, it imports it to supply its refineries. The trade in refined products can change from year to year. That means that global oil prices and shipping circumstances can have a big effect on the Swedish economy, even if Sweden's energy grid is generally low-carbon.
As per Sweden Exporter Data by Import Globals, trade data also shows that crude oil has been one of Sweden's most valuable single imports in recent years. Even when the total value of energy imports goes down (because prices go down), Sweden still requires a steady supply of fuel for transportation, logistics, and some areas of industry.
One way to think about this is that Sweden's energy transition lowers its long-term oil exposure, but in the short and medium term, oil market volatility still affects Swedish costs, especially through freight, mobility, and industrial inputs.
2) Machinery and Transportation Equipment: the "Factory inputs" that Sweden can't Stop
As per Sweden Importer Data by Import Globals, Sweden buys a lot of machinery and transportation equipment from other countries, and these imports have a direct effect on how much industry produces. In 2024, Sweden's imports in this wide category went down, with passenger automobile imports dropping substantially. But it's not easy to "choose" not to import machinery because it includes everything from industrial tools and production lines to spare parts that keep companies running.
This dependency is largely a high-quality one: Sweden buys high-tech equipment from other countries because it works well and is competitive across the world. Not only is there a risk of not having enough, but there is also a risk of timing. If delivery of machinery are late, projects stop and production goes down.
3) Electronics and Telecommunications Equipment: Important for Productivity and Strength
Sweden is no different from other modern economies in that they all rely on electronics. As per Sweden Import Trade Statistics by Import Globals, trade statistics suggest that imports of telecom and transmission equipment are very important. These flows are important for much than just consumer electronics. Telecommunications and electronics are the backbone of industrial automation, energy systems, logistics, and defense-related capabilities.
The weakness here isn't only the price; it's also the policy. Export limits, semiconductor cycles, and geopolitical tensions can all have an effect on the global electronics supply. Even when Sweden's direct imports come "from Europe," the parts that make them up may come from outside Europe, which makes dependencies that aren't obvious.
4) Cars and Car Parts: a Market for Consumers and a Network of Factories that make Cars and Parts
Cars and auto parts are still important imports since Sweden has a well-developed vehicle market and a strong transport and logistics environment. Even if the value of imported passenger cars goes down in a particular year, the overall dependence on them stays the same through parts, accessories, business fleets, and cross-border supply chains.
This is also a traditional inflation channel. As per Sweden Import Shipment Data by Import Globals, changes in currency, shipping costs, and supply limits immediately show up in the pricing and expenses of maintaining vehicles.
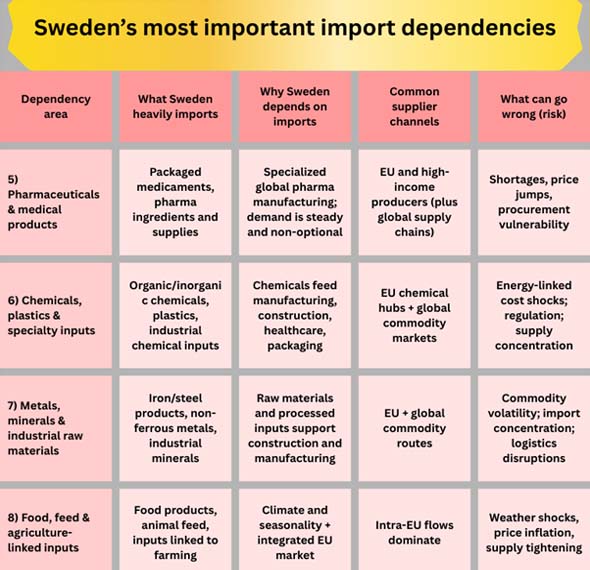
5) Pharmaceuticals: a Dependence that doesn't Handle Change Well
As per Sweden Export Import Global Trade Data by Import Globals, healthcare imports, especially drugs, are some of the least "flexible" demands for imports. During downturns, demand doesn't go down substantially, and substitution can be controlled by regulations, patents, and clinical standards. Recent reports on Swedish trade show that pharmaceutical imports are growing quickly, even while other types of imports are not.
This makes it a top priority for policy to diversify the supply, improve the procurement strategy, and keep buffers for important medicines.
6) Who Sweden Depends on: Partners are Important, but so are "Routes."
Sweden's main trading partners are mostly European, and surrounding industrial sectors and logistics centers play big roles. There is also a nuance to import partner data: some "partner countries" serve as transshipment and distribution centers, which means that the recorded partner may show where items were shipped from (or consigned) rather than where they were made in the first place.
Dependency isn't just about "which country." It's also about "which route," like ports, warehouses, and supply-chain corridors. As per Sweden Import Export Trade Analysis by Import Globals, this is why problems with logistics in important European hubs can affect Swedish supplies, even if the product comes from somewhere else.
Conclusion
Sweden's reliance on imports is not a weakness; it is a sign of a highly productive, globally integrated economy. Crude oil is the most structurally dependent resource for Sweden because it imports crude oil and is still affected by changes in world prices and shipping. Sweden's success depends on more than just energy. It also needs reliable imports of machinery, electronics, vehicles and parts, chemicals, and pharmaceuticals. These are the building blocks of advanced industry and public health.
The practical lesson for businesses is to think of these groups as "risk-managed inputs." When possible, they should use a variety of suppliers, find hidden upstream sources, and make their operations more resilient by using different inventory strategies and transportation plans. For policymakers, the most important things are to make energy transition paths stronger, make sure that crucial medication and technology are always available, and make European and global logistics less vulnerable to choke points. Import Globals is a leading data provider of Sweden Import Export Trade Data.
FAQs
Que. What is Sweden's most important structural import dependency?
Ans. Sweden imports crude oil, which means that its supply chains for crude oil and petroleum are affected by changes in global oil prices and shipping costs.
Que. What is the reason for Sweden's large imports of machinery and equipment?
Ans. Sweden's economy is based on capital and industry. Importing machinery helps with repairs, improvements, and making things.
Que. Does the EU send majority of Sweden's goods?
Ans. A lot of it comes from European supply chains and hubs, but many things contain pieces created outside of Europe, which makes "hidden" upstream dependence.
Que. Which imports are the worse for the well-being of society?
Ans. Pharmaceuticals and essential medical items are limited by alternatives, and interruptions in supply negatively affect healthcare delivery.
Que. Where to get detailed Sweden?
Ans. Visit www.importglobals.com
