- Aug 18, 2025
Global Trade and Market Analysis of Power Generators
A power generator is essentially a machine that transforms mechanical energy into electrical energy, guaranteeing a steady supply of electricity during blackouts or in areas without grid connectivity. As per Power Generators Export Data by Import Globals, Power generators are essential to preserving stability and productivity across a range of industries, whether they are used for emergency backup in hospitals, power supply for distant construction sites, or protecting crucial infrastructure during natural disasters.
Power generators have become much more important as a result of rising global energy demands and frequent disruptions brought on by climatic catastrophes or infrastructure issues. They make it possible for households, companies, and industries to continue operating normally even in the face of power outages. Furthermore, as per Import Data by Import Globals, the varieties and efficiency of generators have expanded due to technological improvements, increasing their adaptability to various fuel sources and environmental regulations. Consequently, the global production and trade of power generators has grown to constitute a substantial portion of the energy equipment market, affecting economies and energy security globally.
Importance of Power Generators
Power generators are indispensable in:
- Disaster relief and emergency power support
- Construction sites, remote industrial operations
- Hospitals, data centers, and infrastructure requiring uninterrupted power
- Countries with unstable power grids
- Military operations and field missions
Because they guarantee a consistent and dependable source of electricity in circumstances where the main power grid is unreliable or unavailable, power generators are essential. Emergency power assistance and disaster relief are two of the most important applications for power generators. As per Power Generators Import Export Trade Data by Import Globals, conventional power lines frequently sustain damage during natural disasters like hurricanes, earthquakes, or floods, leading to extensive outages. To save lives and return things to normal, generators offer instant backup power for communication systems, emergency shelters, and rescue operations.
In remote industrial operations and building sites where grid power may not reach, generators are the main source of electricity for tools, lighting, and heavy machinery. Similar to this, as per Import Custom Data by Import Globals, industries like data centers, hospitals, and vital infrastructure depend significantly on continuous electricity because even a short outage can result in significant data loss or even put lives in danger. In nations with erratic or unreliable electrical systems, generators are also essential because they allow homes and businesses to continue operating normally. Furthermore, portable generators ensure operational preparedness in any area during military operations and field missions by supplying vital power for vehicles, communication devices, and other tactical gear.
Key Components of Power Generators
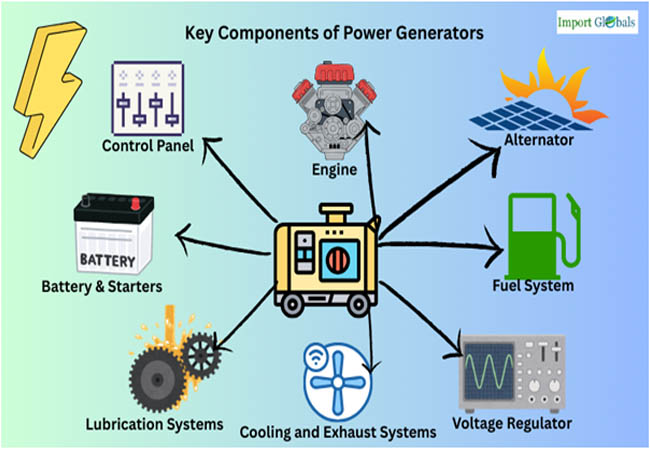
Engine - Fuel is transformed into mechanical energy by the engine.
In a generator, the engine serves as the main source of mechanical energy. To generate combustion energy, it burns fuel, usually natural gas, propane, diesel, or gasoline. The rotors or pistons move as a result of this energy, creating the mechanical force needed to turn the alternator. The generator's total power output capacity is determined by the size and kind of engine.
Alternator - Mechanical energy is transformed into electrical energy by an alternator.
The part that converts the engine's mechanical energy into electrical energy is the alternator, sometimes referred to as the generator head. It is made up of a stator (the stationary element) and a rotor (the moving part). Alternating current (AC) electricity is produced when the rotor spins inside the stator, creating an electromagnetic field.
Fuel System - Holds and Distributes Fuel
When needed, the fuel system supplies and stores fuel for the engine. A fuel tank, pump, fuel lines, and filters are usually included. For the engine to run efficiently, the system makes sure that it gets a steady and clean supply of fuel. Fuel tanks can be external or built-in, depending on the generator's size and intended purpose.
Voltage Regulator - The generator generates electricity at a steady and usable voltage level thanks to the voltage regulator. By regulating the alternator's excitation current, it automatically modifies the voltage output in response to variations in load demand. By doing this, voltage swings that can harm linked equipment are avoided.
Cooling and Exhaust Systems - Maintaining the operating temperature is done by cooling and exhaust systems. While running, generators produce heat, and the cooling system helps control the temperature to avoid overheating. Either liquid or air cooling is an option, depending on the design and size. The exhaust system properly directs dangerous gases, including carbon monoxide, away from the generator by expelling them from the engine.
Lubrication Systems - A lubrication system makes sure that moving parts operate smoothly. The lubrication system disperses oil throughout the engine to lessen wear and friction on engine parts. This system consists of a reservoir, oil pump, and oil filter. Frequent lubrication guarantees smoother, more dependable operation and helps the engine last longer.
Battery and Starter - The initial electrical power required to start the generator engine is supplied by the battery. The battery powers the starter motor, which rotates the engine until it starts up on its own. The generator could not be started manually or automatically without this part.
Control Panel - The control panel acts as the generator’s command center. It displays key information such as voltage, current, frequency, and engine parameters like oil pressure and temperature. As per Power Generators Import Trade Analysis by Import Globals, advanced panels also include safety features, fault alerts, auto-start settings, and remote monitoring capabilities, making it easier to operate and maintain the generator.
Variety and Types of Power Generators
Fuel Types: Hydrogen, Biogas, Solar, Natural Gas, Diesel, and Petrol
The fuel type that a generator uses determines its cost, efficiency, and emissions. While gasoline and diesel are widely used, greener options like solar and hydrogen are becoming more popular.
Application: Standby, Portable, Inverter, Industrial, and Marine Generators. All have distinct uses: industrial/marine generators manage heavy-duty jobs, portable generators are movable, standby units give emergency backup, and inverter kinds offer clean electricity.
Types of Phases: Single - and Three-Phase Because they produce less electricity, single-phase generators are perfect for small offices and households. Three-phase generators provide higher, more reliable power for commercial and industrial applications.
Power Output: Small (1–5 kW), Medium (5–500 kW), and Large (>500 kW) power outputs are available. Large generators are utilized for factories, data centers, or entire buildings; medium-sized generators assist enterprises; and small generators power domestic equipment.
Quality Considerations
As per Exporter Data by Import Globals, quality is crucial when choosing a power generator since it guarantees dependability, security, and long-term performance. To guarantee steady power output, fuel efficiency, and minimal maintenance requirements, high-quality generators are constructed using robust materials, effective engines, and sophisticated control systems. The engine and alternator's build quality, adherence to global safety and emission regulations, noise levels, and warranty or service assistance are important considerations. Purchasing a reliable brand with approved parts guarantees operational safety, lowers downtime, and eventually provides better value.
Manufacturing Process of Power Generators
Design and Engineering – CAD modeling and prototyping: Engineers use CAD software to design generator components and build prototypes. This stage ensures structural accuracy, efficiency, and compliance with industry standards.
Engine Production – Forging, casting, and assembly of the engine: The engine is built through forging and casting metal parts, followed by precise assembly. This includes the crankshaft, cylinder block, pistons, and fuel systems.
Alternator Assembly – Copper winding, stator/rotor creation: The alternator is crafted by winding copper coils and assembling the stator and rotor. This unit converts mechanical motion into electrical energy efficiently.
System Integration – Fitting electrical components and controls: All internal systems, voltage regulators, wiring, batteries, and control panels are integrated. This step ensures the generator functions smoothly as a unified machine.
Enclosure Manufacturing – Weather-proof and soundproof casing: Durable enclosures are built to protect the generator from weather and reduce noise. Materials like steel and sound-absorbing foam are commonly used.
Testing and Quality Checks – Load, safety, emission tests: Each generator undergoes rigorous testing for performance, emissions, safety, and durability. Load tests verify output capacity under different conditions.
Packaging and Shipping – Compliance-based packaging and export: Generators are securely packed with labels and manuals according to international export norms. Shock-proof and moisture-resistant packaging ensures safe global delivery.
Major Exporting Countries of Power Generators
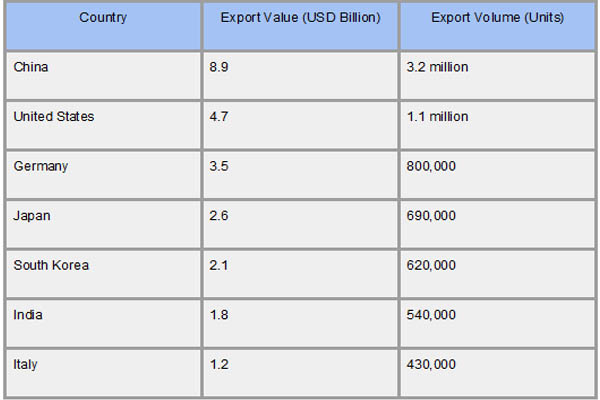
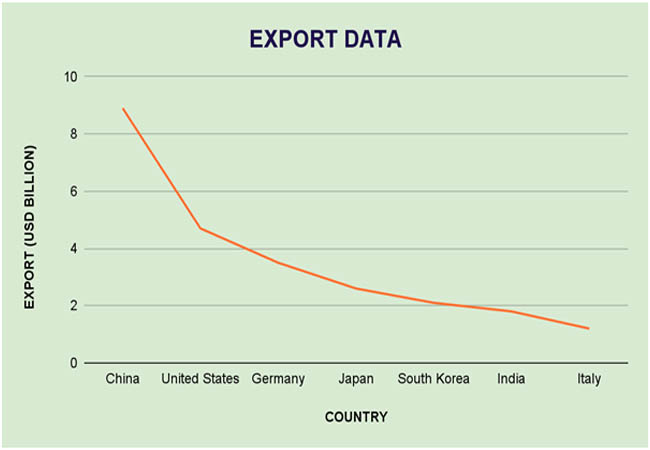
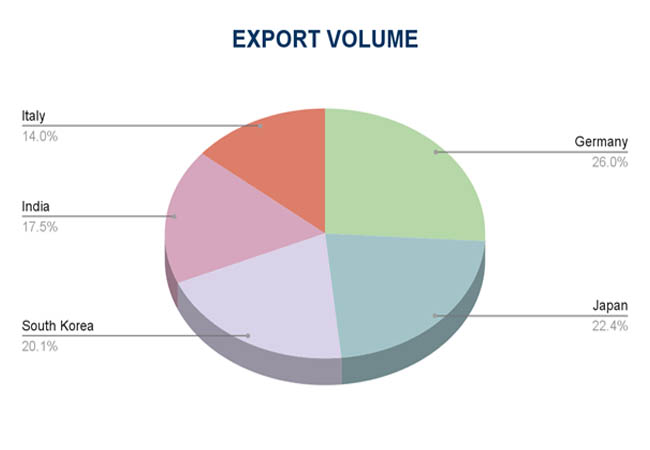
As per Power Generators Importer Data by Import Globals, China, the US, Germany, Japan, and South Korea are the world's top exporters of power generators, thanks to their sophisticated production processes and robust industrial bases. While the United States and Germany concentrate on high-performance, industrial-grade units with superior technology, China leads the industry with a large volume of low-to-medium range generators. South Korea and Japan make major contributions with their small and fuel-efficient cars. Each year, these nations sell generators valued at billions of dollars to areas with increasing infrastructure needs, particularly in Asia, Africa, and Latin America. Strong supply chains, strict quality control procedures, and advancements in clean and hybrid energy technologies all contribute to its export power.
Major Power Generator Manufacturers and Hubs
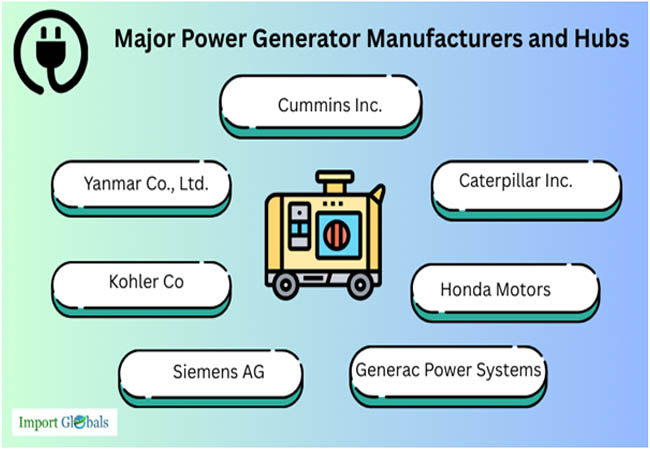
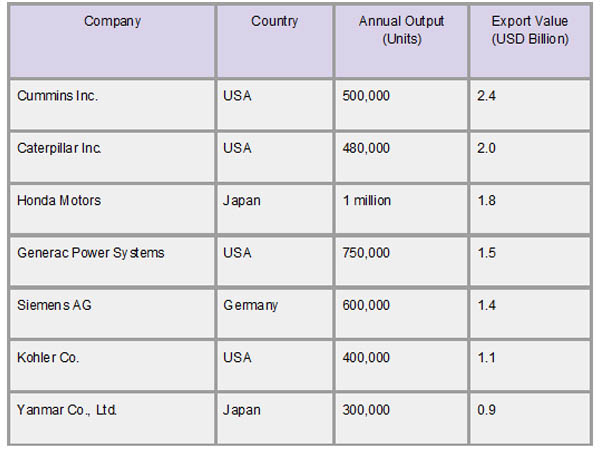
As per Import Trade Statistics by Import Globals, key manufacturers, including Cummins (USA), Caterpillar (USA), Generac (USA), Kohler (USA), Mitsubishi (Japan), Honda (Japan), Siemens (Germany), and Atlas Copco (Sweden), control the majority of the worldwide power generator market. These businesses run sizable production plants in major industrial centers in North America, Europe, and Asia; because of cost advantages and growing demand, China and India are increasingly becoming important manufacturing hubs. These hubs serve both domestic and foreign markets and specialize in a range of sectors, from small portable generators to huge industrial and commercial units. To satisfy international energy and environmental regulations, they are concentrating on developing hybrid, solar-integrated, and low-emission generator types.
Top Importer Countries of Power Generators
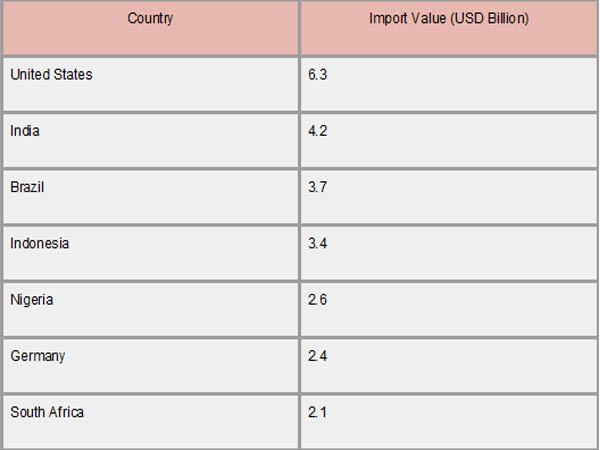
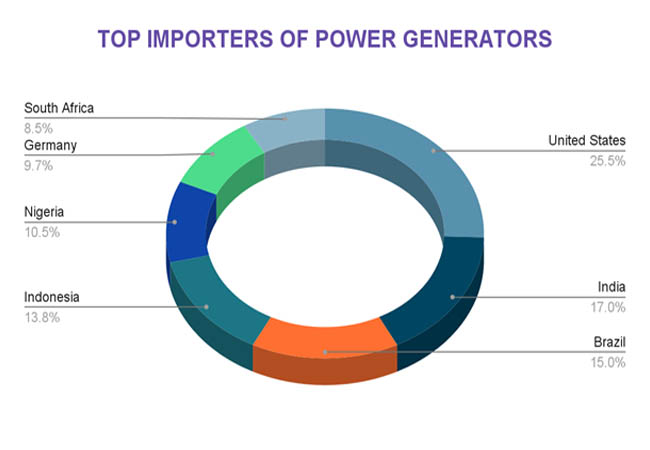
In 2023, the United States led global imports of electric generating sets (HS Code 8502), with a total value of $2.31 billion, followed by Canada at $1.34 billion and the United Kingdom at $1.3 billion. As per Import Shipment Data by Import Globals, these figures underscore the significant demand for power generators in these countries, driven by factors such as infrastructure development, emergency preparedness, and industrial needs. The robust import values reflect the critical role that power generators play in ensuring energy reliability and supporting various sectors across these nations.
Strategic Implications of Global Generator Trade
Energy security, industrial resilience, and catastrophe readiness are all directly impacted by the global trade in power generators, which has important strategic ramifications. Trade dependencies and the requirement for dependable, continuous power, particularly during emergencies or grid instability, must be balanced in nations that depend on imports for vital power infrastructure. Furthermore, as per Import Export Trade Analysis by Import Globals, worldwide concerns about sustainability and environmental compliance are reflected in the move toward cleaner and more efficient generator technologies, such as hybrid, solar-integrated, and low-emission models. While importing nations concentrate on source diversification to reduce supply risks and guarantee ongoing power availability for critical services, nations that have robust manufacturing capacities and export leadership in cutting-edge generator technology enjoy economic and geopolitical advantages.
Conclusion
Around the world, power generators are essential to emergency response, industrial activities, and modern infrastructure. They offer dependable power solutions for a range of applications and situations thanks to their varied types and cutting-edge technologies. As per Export Import Global Trade Data by Import Globals, the interdependence of industrial centers and importing countries, which each support economic expansion and energy security, is demonstrated by the global trade in power generators. As per Import Export Global Data, the industry is positioned for innovation-driven development as demand increases, particularly for cleaner and more efficient models. Stakeholders hoping to navigate and thrive in this crucial industry will need to comprehend quality standards, market dynamics, and strategic trade patterns.
If you are looking for detailed and up-to-date Power Generator Export Data, You Can Contact Import Globals.
FAQs
Que. What fuel types are commonly used in generators?
Ans. Diesel, petrol, natural gas, biogas, and solar hybrids are the most common.
Que. Which country is the largest exporter of power generators?
Ans. China leads with over USD 8.9 billion in exports in 2023.
Que. What factors affect generator quality?
Ans. Durability, efficiency, emission compliance, and noise control.
Que. Are there eco-friendly generator options?
Ans. Yes, solar-powered and inverter generators are greener alternatives.
Que. Which industries rely heavily on power generators?
Ans. Construction, healthcare, IT, telecom, and disaster management sectors.
Que. Where to obtain detailed Power Generator Import Data?
Ans. Visit www.importglobals.com or email info@importglobals.com for more information on up-to-date Power Generator Import Data.
