
- Jul 04, 2025
Uganda Export Data Analysis: Trends, Destinations, and Strategic Insights
According to Import Globals' Uganda Import Custom Data, Uganda's export profile includes in-demand goods like gold, coffee, fish, and oilseeds. The country's economy is primarily based on agriculture, mining, and industry. Uganda's export earnings and trade alliances are anticipated to grow even further as the nation gets ready to start producing commercial oil, establishing it as a major economic player in the East African Community (EAC) and beyond.
General Economy of Uganda: An Overview
Although more than 70% of Uganda's workforce is employed in agriculture, the sector accounts for less than 25% of the country's GDP. The services sector has become the largest contributor to GDP, followed by industry and manufacturing, according to Import Globals' Uganda Import Trade Analysis. Despite external shocks like the COVID-19 epidemic and changes in the price of commodities globally, the nation has maintained consistent economic development over the past ten years, with GDP growth averaging between 4% and 6% yearly. Uganda's gradual transition to a more diversified economy has been largely attributed to its macroeconomic management, infrastructure development, and poverty alleviation initiatives.
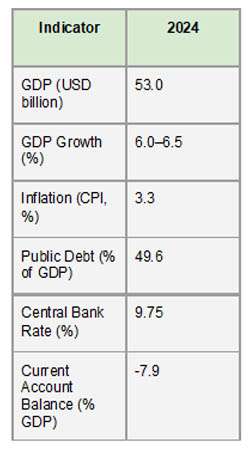
Although more than 70% of Uganda's workforce is employed in agriculture, the sector accounts for less than 25% of the country's GDP. The services sector has become the largest contributor to GDP, followed by industry and manufacturing, according to Import Globals' Uganda Import Trade Analysis. Despite external shocks like the COVID-19 epidemic and changes in the price of commodities globally, the nation has maintained consistent economic development over the past ten years, with GDP growth averaging between 4% and 6% yearly. Uganda's gradual transition to a more diversified economy has been largely attributed to its macroeconomic management, infrastructure development, and poverty alleviation initiatives.
Uganda Export Data Analysis
Between 2020 and 2024, Uganda's export industry grew and diversified significantly. The value of exports dropped from around $5.80 billion in 2020 to $5.48 billion in 2022. But by 2023, exports had risen to $6.60 billion, a 20.43% increase over the year before. According to Import Globals' Uganda Export Data, this upward trend persisted into 2024, when exports hit $7.12 billion, a 7.88% increase over 2023. A major factor in this development was the resurgence of gold exports, which in 2023 ranked as the top export commodity with a value of $2.2 billion.
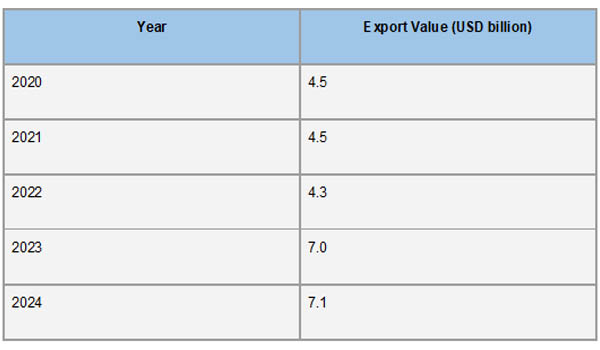
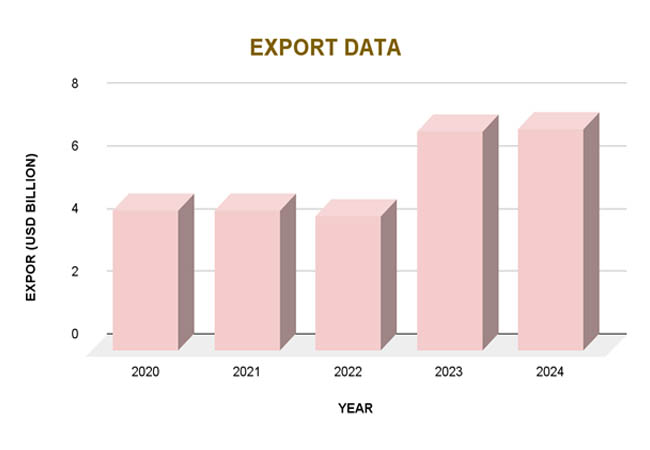
The growing value of manufactured goods, which increased from $1.885 billion in 2022 to $2.526 billion in 2023, demonstrates Uganda's export portfolio's diversification. According to Import Globals' Uganda Import Data, the country's top exports in 2023 were fish ($134 million), coffee ($1.1 billion), cereals ($189 million), mineral fuels ($186.8 million), and ceramic items ($183.3 million). The growth into non-traditional exports like cereals and ceramics shows that the economy is moving in the right direction toward being more resilient and diverse.
Major Export Destinations: Uganda’s Key Partners
A notable uptick in Uganda's exports in 2023 was the country's $2.3 billion in gold exports, which more than tenfold increased from the year before. According to Uganda Import Trade Statistics by Import Globals, the suspension of duties on gold exports and the addition of new processing facilities, such as the Chinese-run Wagagai Mining Ltd in eastern Uganda, were responsible for this impressive development. With 21% of Uganda's total exports, worth over $1.36 billion, going to the United Arab Emirates, the country became the top export destination. Kenya ($736 million), India ($728 million), South Sudan ($536 million), and the Democratic Republic of the Congo ($410 million) were other important economic partners.
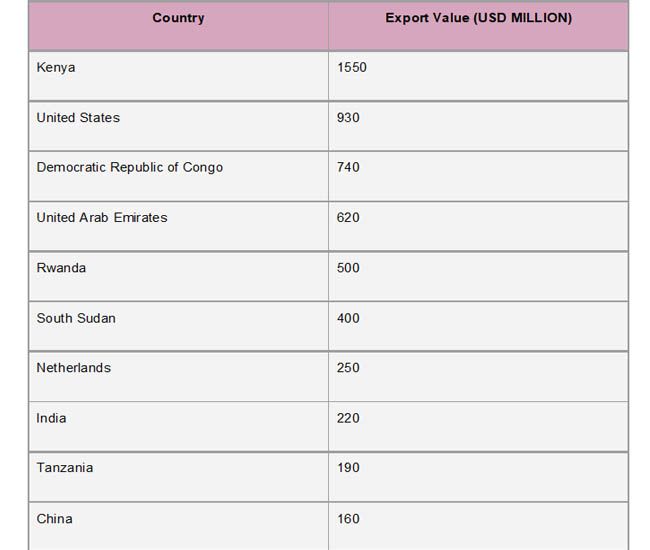
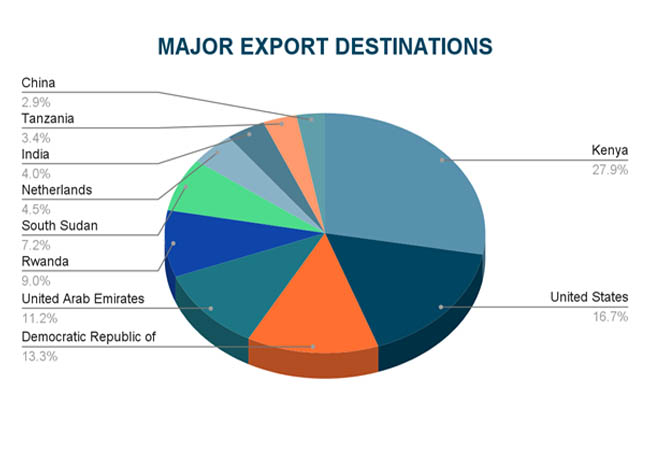
The East African Community (EAC) continued to be a crucial regional market, with South Sudan and Kenya being major importers of Ugandan goods. The diversity of export destinations, which include Asia, the Middle East, and Europe, highlights Uganda's growing global trade footprint, according to Uganda Import Shipment Data From Import Globals. In addition to strengthening the nation's economic resilience, this diversity puts it in a favorable position within the ever-changing world of global trade.
Key Export Products by HS Code
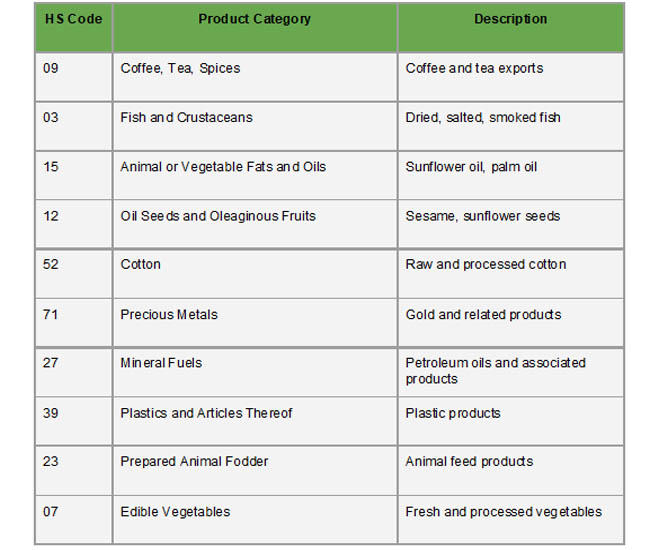
In 2023, Uganda's export portfolio featured a wide variety of goods, all of which were designated by unique Harmonized System (HS) codes. With a value of almost $2.22 billion, or 35% of the nation's total exports, unwrought gold (HS Code 7108) was the most valuable export. Refined petroleum oils (HS Code 2710) at $138 million (2.19%), coffee (HS Code 0901) at $955 million (15.1%), unglazed ceramic tiles (HS Code 6907) at $177 million (2.81%), and cocoa beans (HS Code 1801) at $140 million (2.23%) came next. Other noteworthy exports were tea (HS Code 0902) at $82 million (1.3%) and maize (HS Code 1005) at $135 million (2.15%).
According to Import Globals' Uganda Import Export Trade Analysis, new processing facilities, such as the Chinese-run Wagagai Mining Ltd. in eastern Uganda, and the removal of export duties were responsible for the notable rise in gold exports. Uganda's attempts to broaden its trading base and lessen its dependency on conventional commodities are reflected in the diversity of its export goods. In addition to improving economic resilience, this strategic move puts Uganda in a competitive position on the international stage.
Major Export-Producing Regions in Uganda
- Central Region: The districts of Kampala and Wakiso serve as centers for services, processed foods, and industrial goods.
- Western Region: According to Import Globals' Uganda Export Data, Hoima and Buliisa districts are essential for agriculture and oil extraction.
- Eastern Region: Textiles, sugar, and coffee are the main industries in the districts of Mbale and Jinja.
- Northern Region: The districts of Gulu and Lira are well-known for exporting fish, oilseeds, and cotton.
Uganda's many agricultural regions, each of which makes a distinct contribution to the country's trading portfolio, are the foundation of its export economy. As the industrial and logistical center, the Central Region, which includes the districts of Kampala and Wakiso, makes it easier to process and export a variety of commodities. Districts like Mbale, Sironko, and Kapchorwa in the Eastern Region are known for producing high-quality Arabica coffee, according to Uganda Export Import Global Trade Data by Import Globals. Programs like Sironko's Bayaaya Specialty Coffee empower women farmers and improve the quality of coffee. While the Northern Region, with districts like Gulu and Lira, focuses on cotton, oilseeds, and fish exports, the Western Region, which includes Hoima and Buliisa, is essential for agricultural and oil production.
Strategic Implications
- Oil Production: It is anticipated that the start of commercial crude oil production will increase economic growth to 10.8% in the fiscal year 2025–2026.
- Export Diversification: While coffee and gold continue to be the most popular exports, there is an increasing focus on industrial and agricultural goods, per a report by Import Globals on Uganda Import Data.
- Regional Trade: Market access is improved by close trade relations with nearby nations, including South Sudan, Rwanda, and Kenya.
- Infrastructure Development: To facilitate exports, investments in the oil industry, railroads, and highways are essential.
Uganda's strategic economic path is changing dramatically as a result of the expected start of commercial oil production. The nation is positioned to become a significant oil exporter, with proven reserves of over 6.5 billion barrels; by 2027, production might reach up to 246,000 barrels per day. This development is anticipated to push Uganda's GDP growth into double digits, with estimates showing an acceleration to 10.8% in the fiscal year 2025/2026, according to Uganda Import Export Global Data by Import Globals. At the heart of this plan is the $10 billion East African Crude Oil Pipeline (EACOP), which will carry oil from Uganda to Tanzania's port of Tanga.
Forecast Trends & Pricing Outlook
- Export Growth: As oil production increases, it is expected that exports would reach $7.1 billion in 2024.
- Commodity Prices: Global demand for gold and coffee is anticipated to have a beneficial impact on export earnings, per Import Globals on Uganda Import Export Trade Data.
- Control of Inflation: To promote stable pricing, the central bank's monetary policies seek to keep inflation at or below 5%.
With the expected increase in oil production and the ongoing demand for agricultural products, Uganda's export industry is expected to rise significantly. The start of commercial oil production is predicted to enhance GDP growth to 10.8% by 2025, according to Uganda Export Data, with oil exports being a key contributor to income growth. Coffee exports are expected to rise by 2.76% in the upcoming years as a result of better crop management and favorable weather, while agricultural exports like coffee continue to prosper. Despite changes in world prices and the need for sustainable economic practices, Uganda's export prospects are still bright as it diversifies its export portfolio and makes the most of its oil resources.
Conclusion
In summary, Uganda's export industry is expanding rapidly, propelled by the expected oil boom and the tenacity of agricultural products like fish and coffee. The strategic growth of the oil industry offers both opportunities and problems, even while the nation's economic diversification initiatives are crucial to lowering dependency on a small number of vital commodities. In the upcoming years, Uganda might strengthen its position as a regional and international trade actor, promoting sustainable growth and boosting economic resilience, with sustained investments in value addition and infrastructure.
If you are looking for a detailed and up-to-date Uganda Import Export Trade Analysis, You Can Contact Import Globals.
FAQs
Que: What are the main exports from Uganda?
Ans: Gold, coffee, fish, tea, and vegetable oils are among Uganda's top exports.
Que: Who are the key trading partners of Uganda?
Ans: The United States, Kenya, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, and the United Arab Emirates are important export markets.
Que: What is the anticipated economic impact of oil production in Uganda?
Ans: It is projected that the onset of commercial oil production will greatly accelerate economic expansion and export earnings.
Que: What policies does Uganda have in place to manage inflation?
Ans: To keep inflation within the 5% target range, the Bank of Uganda conducts a cautious monetary policy, modifying the central bank rate.
Que. Where to obtain detailed Uganda Export Data?
Ans. Visit www.importglobals.com or email info@importglobals.com for more information on up-to-date Uganda Export Data.
